Hypergravity enhances the therapeutic effect of dexamethasone in allergic asthma and rhinitis animal model
- PMID: 29772010
- PMCID: PMC5957331
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197594
Hypergravity enhances the therapeutic effect of dexamethasone in allergic asthma and rhinitis animal model
Abstract
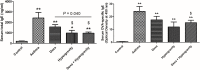
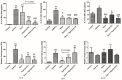
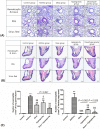
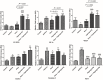
We investigated whether the therapeutic effects of dexamethasone for allergic asthma and rhinitis were enhanced in mice when exposed to hypergravity. Forty mice were divided into 5 groups (n = 8/group): Control group received saline intraperitoneally (i.p.) and intranasally (i.n.); Asthma group received i.p./i.n. ovalbumin (OVA) for inducing allergic asthma/rhinitis; Dexa group received i.n. dexamethasone (0.75 mg/kg) 30 minutes before each OVA challenge; Hypergravity group was subjected to allergic asthma/rhinitis as well as exposed to 5 G hypergravity for 30 days; Finally in Dexa/Hypergravity group, hypergravity and dexamethasone were used simultaneously during induction of allergic asthma/rhinitis. Dexa group and Hypergravity group showed a significant decrease in serum total IgE levels compared to the Asthma group (p<0.05). Dexa/Hypergravity group showed greater IgE decrease compared with Dexa group (p = 0.040). Compared with the monotherapy groups, Dexa/Hypergravity group showed significantly fewer eosinophils in BAL fluid (p<0.05). Dexa/Hypergravity group showed significantly decreased eosinophilic infiltration into the lungs and nasal cavity (p<0.05). EC-SOD (extracellular superoxide dismutase) expression was significantly upregulated in the Hypergravity group and Dexa/Hypergravity group, compared with the Dexa group (p<0.05). In conclusion, hypergravity enhanced the therapeutic effect of dexamethasone in a murine model of allergic asthma and rhinitis. Therefore, combination could be a promising strategy, and one of its mechanisms could be up-regulation of EC-SOD expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

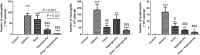
References
-
- Minois N. The hormetic effects of hypergravity on longevity and aging. Dose-Response Publ Int Hormesis Soc. 2006;4: 145–154. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.05-008.Minois - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev. 2008;7: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2007.08.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pecaut MJ, Miller GM, Nelson GA, Gridley DS. Hypergravity-induced immunomodulation in a rodent model: hematological and lymphocyte function analyses. J Appl Physiol. 2004;97: 29–38. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01304.2003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ling S-K, Wang R, Dai Z-Q, Nie J-L, Wang H-H, Tan Y-J, et al. Pretreatment of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with a combination of hypergravity and 5-azacytidine enhances therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction. Biotechnol Prog. 2011;27: 473–482. doi: 10.1002/btpr.558 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou S, Zu Y, Sun Z, Zhuang F, Yang C. Effects of Hypergravity on Osteopontin Expression in Osteoblasts. PloS One. 2015;10: e0128846 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128846 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

