A task-invariant cognitive reserve network
- PMID: 29772378
- PMCID: PMC6409097
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.05.033
A task-invariant cognitive reserve network
Abstract
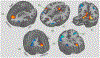
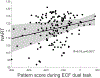
The concept of cognitive reserve (CR) can explain individual differences in susceptibility to cognitive or functional impairment in the presence of age or disease-related brain changes. Epidemiologic evidence indicates that CR helps maintain performance in the face of pathology across multiple cognitive domains. We therefore tried to identify a single, "task-invariant" CR network that is active during the performance of many disparate tasks. In imaging data acquired from 255 individuals age 20-80 while performing 12 different cognitive tasks, we used an iterative approach to derive a multivariate network that was expressed during the performance of all tasks, and whose degree of expression correlated with IQ, a proxy for CR. When applied to held out data or forward applied to fMRI data from an entirely different activation task, network expression correlated with IQ. Expression of the CR pattern accounted for additional variance in fluid reasoning performance over and above the influence of cortical thickness, and also moderated between cortical thickness and reasoning performance, consistent with the behavior of a CR network. The identification of a task-invariant CR network supports the idea that life experiences may result in brain processing differences that might provide reserve against age- or disease-related changes across multiple tasks.
Keywords: Cognitive aging; Cortical thickness; IQ; Multivariate imaging analysis; fMRI.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
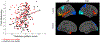
References
-
- Alexander GE, Moeller JR, 1994. Application of the Scaled Subprofile Model to functional imaging in Neuropsychiatric disorders: a principal component approach. Hum. Brain Mapp 2, 79–94.
-
- Bennett DA, Wilson RS, Schneider JA, Evans DA, Mendes De Leon CF, Arnold SE, Barnes LL, Bienias JL, 2003. Education modifies the relation of AD pathology to level of cognitive function in older persons. Neurology 60 (12), 1909–1915. - PubMed
-
- Brayne C, Ince PG, Keage HAD, McKeith IG, Matthews FE, Polvikoski T, Sulkava R, 2010. Education, the brain and dementia: neuroprotection or compensation? EClipSE Collab. Members 133, 2210–2216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

