Duality of estrogen receptor β action in cancer progression
- PMID: 29772419
- PMCID: PMC8008732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2018.05.001
Duality of estrogen receptor β action in cancer progression
Abstract
The physiological actions of estrogens are primarily mediated by the nuclear hormone receptors estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and beta (ERβ). Activities of these nuclear steroid hormone receptors in etiology and progression of many hormone-responsive cancers are well-established, yet the specific role of each receptor, and their various expressed isoforms, in estrogen-responsive cancers remains unclear. Recent advances in nuclear receptor profiling, characterization of expressed splice variants, and the availability of new experimental cancer models, has extended the understanding of the complex interplay between the differentially expressed nuclear estrogen receptors. In this review, we discuss proposed roles of ERβ in several subtypes of cancers that lack significant ERα expression and define current understanding of how different ERs collaborate to regulate cellular processes.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing declared.
Figures
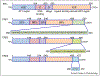
References
-
- Colditz GA: Relationship between estrogen levels, use of hormone replacement therapy, and breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1998, 90:814–823. - PubMed
-
- Thomas C, Gustafsson JÅ: The different roles of ER subtypes in cancer biology and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2011, 11:597–608. - PubMed
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Treuter E, Warner M, Hartman J, Tujague M, Stro A: Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 2007, 87:905–931. - PubMed
-
- Kuiper GGJM: Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor. Endocrinology 1998, 139:4252–4263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

