Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Entry by a Keggin Polyoxometalate
- PMID: 29772712
- PMCID: PMC5977258
- DOI: 10.3390/v10050265
Inhibition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Entry by a Keggin Polyoxometalate
Abstract
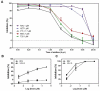
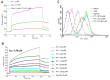
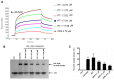
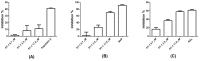
Here, we report the anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) potency and underlying mechanisms of a Keggin polyoxometalate (PT-1, K₆HPTi₂W10O40). Our findings showed that PT-1 exhibited highly potent effects against a diverse group of HIV type 1 (HIV-1) strains and displayed low cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. The time-addition assay revealed that PT-1 acted at an early stage of infection, and these findings were supported by the observation that PT-1 had more potency against Env-pseudotyped virus than vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVG) pseudotyped virus. Surface plasmon resonance binding assays and flow cytometry analysis showed that PT-1 blocked the gp120 binding site in the CD4 receptor. Moreover, PT-1 bound directly to gp41 NHR (N36 peptide), thereby interrupting the core bundle formation of gp41. In conclusion, our data suggested that PT-1 may be developed as a new anti-HIV-1 agent through its effects on entry inhibition.
Keywords: CD4; Keggin polyoxometalate; entry inhibition; gp41 NHR; human immunodeficiency virus type 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ADS-J1 inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 entry by interacting with the gp41 pocket region and blocking fusion-active gp41 core formation.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Dec;53(12):4987-98. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00670-09. Epub 2009 Sep 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19786602 Free PMC article.
-
HbAHP-25, an In-Silico Designed Peptide, Inhibits HIV-1 Entry by Blocking gp120 Binding to CD4 Receptor.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 27;10(4):e0124839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124839. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25915507 Free PMC article.
-
Role for the disulfide-bonded region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 in receptor-triggered activation of membrane fusion function.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 16;394(4):904-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.071. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20230797
-
Progress in targeting HIV-1 entry.Drug Discov Today. 2005 Aug 15;10(16):1085-94. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03550-6. Drug Discov Today. 2005. PMID: 16182193 Review.
-
HIV-1 entry inhibitors in the side pocket.Cell. 1999 Oct 29;99(3):243-6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81655-4. Cell. 1999. PMID: 10555140 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Secondary metabolites produced by endophytic fungi, Alternaria alternata, as potential inhibitors of the human immunodeficiency virus.Front Genet. 2022 Dec 13;13:1077159. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1077159. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36583026 Free PMC article.
-
Increased in vitro Anti-HIV Activity of Caffeinium-Functionalized Polyoxometalates.ChemMedChem. 2021 Sep 6;16(17):2727-2730. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100281. Epub 2021 May 26. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33908695 Free PMC article.
-
New composition of tungsten has a broad range of antiviral activity.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2022 Jan-Dec;30:20402066221090061. doi: 10.1177/20402066221090061. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35392696 Free PMC article.
-
Developments in Exploring Fungal Secondary Metabolites as Antiviral Compounds and Advances in HIV-1 Inhibitor Screening Assays.Viruses. 2023 Apr 23;15(5):1039. doi: 10.3390/v15051039. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium Polyoxotungstate Inhibits the Replication of Influenza Virus by Blocking the Nuclear Import of vRNP.Microorganisms. 2024 May 17;12(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051017. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792846 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

