Outcomes of conventional phacoemulsification versus femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery in eyes with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy
- PMID: 29773458
- PMCID: PMC5997572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.03.023
Outcomes of conventional phacoemulsification versus femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery in eyes with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the outcomes in eyes with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy after standard phacoemulsification with those of femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery.
Setting: Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, Florida, USA.
Design: Retrospective case series.
Methods: Charts from patients diagnosed with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy who had phacoemulsification cataract surgery at Bascom Palmer Eye Institute between January 1, 2014, and January 1, 2017, were reviewed. The Institutional Review Board, University of Miami Human Subjects Research Office, approved the study protocol. Complicated surgeries and cases with concurrent keratoplasty, previous keratoplasty or glaucoma surgery, or a follow-up shorter than 3 months were excluded. The corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), central corneal thickness (CCT), and corneal edema at each visit were analyzed. Clinically significant corneal decompensation was defined by corneal edema with CDVA worse than 20/50 lasting more than 3 months, any case resulting in keratoplasty, or both.
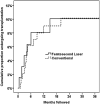
Results: The study comprised 207 eyes of 207 patients (64 femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery, 143 conventional phacoemulsification). Demographics, baseline guttata and cataract grades, and follow-up time (mean 30 months) were similar between groups (P > .05). The proportion of cases progressing to clinically significant decompensation (13%) was similar between groups (P > .05). Univariate Cox survival analysis also found no difference (hazard ratio, 1.0; 95% confidence interval, 0.4-2.7; P = .96).
Conclusions: Compared with conventional phacoemulsification, femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery did not lower the rate of corneal decompensation in eyes with mild to moderate Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy.
Copyright © 2018 ASCRS and ESCRS. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bourne RRA, Minassian DC, Dart JKG, Rosen P, Kaushal S, Wingate N. Effect of cataract surgery on the corneal endothelium; modern phacoemulsification compared with extracapsular cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 2004;111:679–685. - PubMed
-
- Lundberg B, Jonsson M, Behndig A. Postoperative corneal swelling correlates strongly to corneal endothelial cell loss after phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:1035–1041. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Risk factors for corneal endothelial injury during phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1996;22:1079–1084. - PubMed
-
- Walkow T, Anders N, Klebe S. Endothelial cell loss after phacoemulsification: relation to preoperative and intraoperative parameters. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:727–732. - PubMed
-
- Giasson CJ, Solomon LD, Polse KA. Morphometry of corneal endothelium in patients with corneal guttata. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1469–1475. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

