Learning lessons in sepsis from the children
- PMID: 29773678
- PMCID: PMC5974510
- DOI: 10.15252/msb.20188335
Learning lessons in sepsis from the children
Abstract
Sepsis research has had relatively limited therapeutic success so far. In their recent study, Kobzik and colleagues (Joachim et al, 2018) identify novel drug‐sensitive pathways in sepsis, derived exclusively from patient data. Their strategy is based on the analysis of a naturally sepsis‐resistant population (pre‐puberty children) and on the implementation of a novel‐rich Pathway Drug Network, constructed from human gene expression data enriched in drug–pathway–gene clusters.
Figures
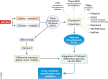
Comment on
-
The relative resistance of children to sepsis mortality: from pathways to drug candidates.Mol Syst Biol. 2018 May 17;14(5):e7998. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177998. Mol Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29773677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beura LK, Hamilton SE, Bi K, Schenkel JM, Odumade OA, Casey KA, Thompson EA, Fraser KA, Rosato PC, Filali‐Mouhim A, Sekaly RP, Jenkins MK, Vezys V, Haining WN, Jameson SC, Masopust D (2016) Normalizing the environment recapitulates adult human immune traits in laboratory mice. Nature 532: 512–516 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG, Mindrinos MN, Baker HV, Xu WH, Richards DR, McDonald‐Smith GP, Gao H, Hennessy L, Finnerty CC, Lopez CM, Honari S, Moore EE, Minei JP, Cuschieri J, Bankey PE, Johnson JL, Sperry J, Nathens AB et al (2013) Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110: 3507–3512 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Watson RS, Carcillo JA, Linde‐Zwirble WT, Clermont G, Lidicker J, Angus DC (2003) The epidemiology of severe sepsis in children in the United States. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167: 695–701 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

