On the Drive Specificity of Freudian Drives for the Generation of SEEKING Activities: The Importance of the Underestimated Imperative Motor Factor
- PMID: 29774002
- PMCID: PMC5943553
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00616
On the Drive Specificity of Freudian Drives for the Generation of SEEKING Activities: The Importance of the Underestimated Imperative Motor Factor
Abstract
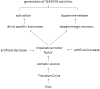
Doubters of Freud's theory of drives frequently mentioned that his approach is outdated and therefore cannot be useful for solving current problems in patients with mental disorders. At present, many scientists believe that affects rather than drives are of utmost importance for the emotional life and the theoretical framework of affective neuroscience, developed by Panksepp, strongly underpinned this view. Panksepp evaluated seven so-called command systems and the SEEKING system is therein of central importance. Panksepp used Pankseppian drives as inputs for the SEEKING system but noted the missing explanation of drive-specific generation of SEEKING activities in his description. Drive specificity requires dual action of the drive: the activation of a drive-specific brain area and the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Noticeably, as Freud claimed drive specificity too, it was here analyzed whether a Freudian drive can evoke the generation of drive-specific SEEKING activities. Special importance was addressed to the imperative motor factor in Freud's drive theory because Panksepp's formulations focused on neural pathways without specifying underlying neurotransmitter/endocrine factors impelling motor activity. As Panksepp claimed sleep as a Pankseppian drive, we firstly had to classified sleep as a Freudian drive by using three evaluated criteria for a Freudian drive. After that it was possible to identify the imperative motor factors of hunger, thirst, sex, and sleep. Most importantly, all of these imperative motor factors can both activate a drive-specific brain area and release dopamine from dopaminergic neurons, i.e., they can achieve the so-called drive specificity. Surprisingly, an impaired Freudian drive can alter via endocrinological pathways the concentration of the imperative motor factor of a second Freudian drive, obviously in some independence to the level of the metabolic deficit, thereby offering the possibility to modulate the generation of SEEKING activities of this second Freudian drive. This novel possibility might help to refine the general understanding of the action of Freudian drives. As only imperative motor factors of Freudian drives can guarantee drive specificity for the generation of SEEKING activities, the impact of Freud's construct Eros (with its constituents hunger, thirst, sex, and sleep) should be revisited.
Keywords: adenosine; angiotensin II; drive specificity; ghrelin; testosterone.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials