Digital Museum of Retinal Ganglion Cells with Dense Anatomy and Physiology
- PMID: 29775596
- PMCID: PMC6556895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.040
Digital Museum of Retinal Ganglion Cells with Dense Anatomy and Physiology
Abstract
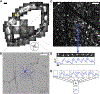
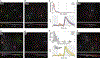
When 3D electron microscopy and calcium imaging are used to investigate the structure and function of neural circuits, the resulting datasets pose new challenges of visualization and interpretation. Here, we present a new kind of digital resource that encompasses almost 400 ganglion cells from a single patch of mouse retina. An online "museum" provides a 3D interactive view of each cell's anatomy, as well as graphs of its visual responses. The resource reveals two aspects of the retina's inner plexiform layer: an arbor segregation principle governing structure along the light axis and a density conservation principle governing structure in the tangential plane. Structure is related to visual function; ganglion cells with arbors near the layer of ganglion cell somas are more sustained in their visual responses on average. Our methods are potentially applicable to dense maps of neuronal anatomy and physiology in other parts of the nervous system.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; calcium imaging; cell type; crowdsourcing; electron microscopy; ganglion cell; inner plexiform layer; mouse; online atlas; retina.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




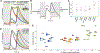
References
-
- Amunts K, Lepage C, Borgeat L, Mohlberg H, Dickscheid T, Rousseau M-É, Bludau S, Bazin P-L, Lewis LB, Oros-Peusquens A-M, et al. (2013). BigBrain: An ultrahigh-resolution 3D human brain model. Science, 340(6139):1472–1475. - PubMed
-
- Arthur D and Vassilvitskii S (2007). k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the 18th annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete algorithms, pages 1027–1035. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
-
- Ascoli GA, Donohue DE, and Halavi M (2007). NeuroMorpho.org: A central resource for neuronal morphologies. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(35):9247–9251. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badea TC and Nathans J (2004). Quantitative analysis of neuronal morphologies in the mouse retina visualized by using a genetically directed reporter. J Comp Neurol, 480(4):331–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

