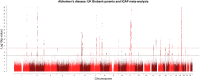
GWAS on family history of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29777097
- PMCID: PMC5959890
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-018-0150-6
GWAS on family history of Alzheimer's disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: GWAS on family history of Alzheimer's disease.Transl Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 6;9(1):161. doi: 10.1038/s41398-019-0498-2. Transl Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31171767 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a public health priority for the 21st century. Risk reduction currently revolves around lifestyle changes with much research trying to elucidate the biological underpinnings. We show that self-report of parental history of Alzheimer's dementia for case ascertainment in a genome-wide association study of 314,278 participants from UK Biobank (27,696 maternal cases, 14,338 paternal cases) is a valid proxy for an AD genetic study. After meta-analysing with published consortium data (n = 74,046 with 25,580 cases across the discovery and replication analyses), three new AD-associated loci (P < 5 × 10-8) are identified. These contain genes relevant for AD and neurodegeneration: ADAM10, BCKDK/KAT8 and ACE. Novel gene-based loci include drug targets such as VKORC1 (warfarin dose). We report evidence that the association of SNPs in the TOMM40 gene with AD is potentially mediated by both gene expression and DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex. However, it is likely that multiple variants are affecting the trait and gene methylation/expression. Our discovered loci may help to elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying AD and, as they contain genes that are drug targets for other diseases and disorders, warrant further exploration for potential precision medicine applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG054014/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12011/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L015382/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG049508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG052411/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous