Palliative and end-of-life care for heart failure patients in an aging society
- PMID: 29779361
- PMCID: PMC6234394
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2018.106
Palliative and end-of-life care for heart failure patients in an aging society
Abstract
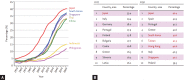
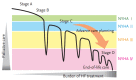
The populations of Asian countries are expected to age rapidly in the near future, with a dramatic increase in the number of heart failure (HF) patients also anticipated. The need for palliative and end-of-life care for elderly patients with advanced HF is currently recognized in aging societies. However, palliative care and active treatment for HF are not mutually exclusive, and palliative care should be provided to reduce suffering occurring at any stage of symptomatic HF after the point of diagnosis. HF patients are at high risk of sudden cardiac death from the early stages of the disease onwards. The decision of whether to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the event of an emergency is challenging, especially in elderly HF patients, because of the difficulty in accurately predicting the prognosis of the condition. Furthermore, advanced HF patients are often fitted with a device, and device deactivation at the end of life is a complicated process. Treatment strategies should thus be discussed by multi-disciplinary teams, including palliative experts, and should consider patient directives to address the problems discussed above. Open communication with the HF patient regarding the expected prognosis, course, and treatment options will serve to support the patient and aid in future planning.
Keywords: Aged; Aging; End-of-life care; Heart failure; Palliative care.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division . New York: United Nations; 2017. World population prospects: the 2017 revision [Internet] [cited 2018 Mar 22]. Available from: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/
-
- Shimokawa H, Miura M, Nochioka K, Sakata Y. Heart failure as a general pandemic in Asia. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17:884–892. - PubMed
-
- Cabinet office, Government of Japan . Tokyo (JP): Cabinet office, Government of Japan; c2014. Annual report on the aging society: 2016 (summary) [Internet] [cited 2018 Mar 22]. Available from: http://www8.cao.go.jp/kourei/english/annualreport/2016/pdf/c1-1.pdf.
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division . New York: United Nations; 2017. World population prospects: the 2015 revision [Internet] [cited 2018 Mar 22]. Available from: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
