Disease Heritability Inferred from Familial Relationships Reported in Medical Records
- PMID: 29779949
- PMCID: PMC6015747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.032
Disease Heritability Inferred from Familial Relationships Reported in Medical Records
Abstract
Heritability is essential for understanding the biological causes of disease but requires laborious patient recruitment and phenotype ascertainment. Electronic health records (EHRs) passively capture a wide range of clinically relevant data and provide a resource for studying the heritability of traits that are not typically accessible. EHRs contain next-of-kin information collected via patient emergency contact forms, but until now, these data have gone unused in research. We mined emergency contact data at three academic medical centers and identified 7.4 million familial relationships while maintaining patient privacy. Identified relationships were consistent with genetically derived relatedness. We used EHR data to compute heritability estimates for 500 disease phenotypes. Overall, estimates were consistent with the literature and between sites. Inconsistencies were indicative of limitations and opportunities unique to EHR research. These analyses provide a validation of the use of EHRs for genetics and disease research.
Keywords: data mining; disease heritability; electronic health record; familial relationships; family history; genetics; observational databases.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
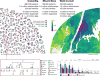

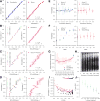
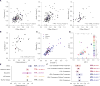
Comment in
-
Estimating heritability without genetic testing.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Jul;19(7):403. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0021-2. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29795126 No abstract available.
-
Disease Heritability Studies Harness the Healthcare System to Achieve Massive Scale.Cell. 2018 Jun 14;173(7):1568-1570. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.053. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29906443
References
-
- Bederson JB, Awad IA, Wiebers DO, Piepgras D, Haley EC, Brott T, Hademenos G, Chyatte D, Rosenwasser R, Caroselli C. Recommendations for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms - A statement for healthcare professionals from the Stroke Council of the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2000;102:2300–2308. - PubMed
-
- Birkhead GS, Klompas M, Shah NR. Uses of electronic health records for public health surveillance to advance public health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:345–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

