Systems Biology-Based Investigation of Host-Plasmodium Interactions
- PMID: 29779985
- PMCID: PMC7028355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2018.04.003
Systems Biology-Based Investigation of Host-Plasmodium Interactions
Abstract
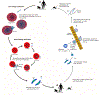
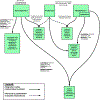
Malaria is a serious, complex disease caused by parasites of the genus Plasmodium. Plasmodium parasites affect multiple tissues as they evade immune responses, replicate, sexually reproduce, and transmit between vertebrate and invertebrate hosts. The explosion of omics technologies has enabled large-scale collection of Plasmodium infection data, revealing systems-scale patterns, mechanisms of pathogenesis, and the ways that host and pathogen affect each other. Here, we provide an overview of recent efforts using systems biology approaches to study host-Plasmodium interactions and the biological themes that have emerged from these efforts. We discuss some of the challenges in using systems biology for this goal, key research efforts needed to address those issues, and promising future malaria applications of systems biology.
Keywords: Plasmodium; host–pathogen interaction; malaria; omics; systems biology.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Baird JK (2009) Malaria zoonoses. Travel Med Infect Dis 7 (5), 269–77. - PubMed
-
- WHO (2016) Malaria World Report.
-
- Wanjek C (2011) Systems Biology as Defined by the NIH. The NIH Catalyst 19 (6).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

