Food-specific IgGs Are Highly Increased in the Sera of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Are Clinically Relevant to the Pathogenesis
- PMID: 29780153
- PMCID: PMC6207831
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9377-17
Food-specific IgGs Are Highly Increased in the Sera of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Are Clinically Relevant to the Pathogenesis
Abstract
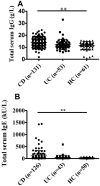
Objective Dietary antigens are common luminal antigens in the gastrointestinal tract and have been considered to contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We analyzed the levels of food-specific IgGs against a variety of dietary antigens, explored the clinical relevance of food allergy to the pathogenesis of IBD, and investigated whether or not infliximab (IFX) treatment could regulate the immune responses induced by dietary antigens. Methods A total of 301 IBD patients, including 201 patients with Crohn's disease (CD) and 100 patients with ulcerative colitis (UC), were recruited, and their serum food-specific IgGs against 14 food antigens were detected by a semi-quantitative enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Total serum IgG and IgE levels were measured by immunonephelometry and fluorescent enzyme immunoassay, respectively. Simultaneously, the relevant medical records and clinical data were collected for further analyses. Results Food-specific IgGs against egg, milk, wheat, corn, rice, tomato, codfish, and soybean antigens were found to be significantly increased in the sera of CD patients compared with UC patients and healthy controls (p<0.01). The levels of total serum IgG and IgE were also significantly higher in CD patients than in healthy controls (p<0.01). The titers of corn- and tomato-specific IgGs were found to be significantly correlated with total serum IgG in CD patients (p<0.05), while the titers of egg-, milk-, and wheat-specific IgGs were correlated with total serum IgE (p<0.05). Interestingly, IFX therapy was able to down-regulate the food-specific IgG-mediated immune response markedly in active CD patients. Conclusion Food-specific IgGs against egg, milk, wheat, corn, rice, tomato, codfish, and soybean are highly increased in the sera of CD patients. IFX treatment was able to down-regulate the levels of food-specific IgGs by suppressing intestinal inflammation and promoting mucosal healing. Therefore, food-specific IgGs may serve as an important approach in the diagnosis and management of food allergy in IBD.
Keywords: food antigens; food-specific IgGs; inflammatory bowel disease; total serum IgE; total serum IgG.
Figures



Comment in
-
Food-specific IgG Antibodies in Crohn's Disease: What Came First, the Chicken or the Egg?Intern Med. 2019 Jul 15;58(14):2123. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2379-18. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30918191 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Crohn's disease. Lancet 380: 1590-1605, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Farrell RJ, Peppercorn MA. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 359: 331-340, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Zhou G, Yu L, Fang L, et al. . CD177+ neutrophils as functionally activated neutrophils negatively regulate IBD. Gut 67: 1052-1103, 2018. - PubMed
-
- He C, Yu T, Shi Y, et al. . MicroRNA 301A promotes intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated cancer development by inhibiting BTG1. Gastroenterology 152: 1434-1448, 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

