A useful alternative surgical technique to reconstructing large defects following excision of recurrent pilonidal sinus disease in the intergluteal region: An operative approach for the transverse lumbar artery perforator flap
- PMID: 29781208
- PMCID: PMC7949996
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12894
A useful alternative surgical technique to reconstructing large defects following excision of recurrent pilonidal sinus disease in the intergluteal region: An operative approach for the transverse lumbar artery perforator flap
Abstract
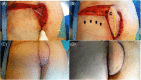
The reconstruction of defects in the intergluteal region following pilonidal sinus excision is challenging due to its anatomical location, close proximity to the anus, and being a high-tension area prone to wound-healing problems. Excision and primary closure is known to carry a higher risk of recurrence and subsequent complications compared with using nearby local healthy tissue, such as a flap, to reconstruct defect. Extra due diligence should be given to patient selection and flap choice when deciding the reconstruction of a defect. The senior author, who has briefly reviewed complication rates in previous published literature, prefers the transverse lumbar artery perforator (TLAP) flap for reconstruction following pilonidal sinus excision in the intergluteal region. This paper illustrates the operative approach used by the senior author when raising a TLAP flap.
Keywords: operative approach; pilonidal sinus intergluteal region.
© 2018 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Idea and innovation: Secure fixation between dermis and periosteum using perforator flap to prevent recurrence of pilonidal sinus disease.Int Wound J. 2019 Jun;16(3):862-865. doi: 10.1111/iwj.12981. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int Wound J. 2019. PMID: 30240147 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Pilonidal Sinus Disease with the Aesthetically Shaped Parasacral Perforator Flap: Multicenter Evaluation of 228 Patients.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Oct;144(4):971-980. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006087. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 31568314
-
Prospective evaluation of a single-sided innervated gluteal artery perforator flap for reconstruction for extensive and recurrent pilonidal sinus disease: functional, aesthetic, and patient-reported long-term outcomes.World J Surg. 2012 Sep;36(9):2230-6. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1639-4. World J Surg. 2012. PMID: 22552500
-
A comparison of flap reconstruction vs the laying open technique or excision and direct suture for pilonidal sinus disease: A meta-analysis of randomised studies.Int Wound J. 2019 Oct;16(5):1119-1135. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13163. Epub 2019 Jun 23. Int Wound J. 2019. PMID: 31230414 Free PMC article.
-
Contralateral Limberg flap reconstruction for pilonidal disease recurrence.Asian J Surg. 2019 Aug;42(8):787-791. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2018.12.008. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Asian J Surg. 2019. PMID: 30711442 Review.
References
-
- Mathur B, Tan S, Bhat F, Rozen W. The transverse lumbar perforator flap: an anatomic and clinical study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(6):770. - PubMed
-
- Kato H, Hasegawa M, Takada T, Tori S. The lumbar artery perforator based island flap: anatomical study and case reports. Br J Plast Surg. 1999;52:541‐546. - PubMed
-
- Peters K, Blondeel P, Lobo F, van Landuyt K. Early experience with the free lumbar artery perforator flap for breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68:1112‐1119. - PubMed
-
- Rawat S, Mathur B. Transverse lumbar flap for sacral bed sores. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;88:154e8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

