The analgesic efficacy and pharmacokinetics of epidural oxycodone after gynaecological laparotomy: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy comparison with intravenous administration
- PMID: 29782641
- PMCID: PMC6089810
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13643
The analgesic efficacy and pharmacokinetics of epidural oxycodone after gynaecological laparotomy: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy comparison with intravenous administration
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to compare the analgesic efficacy of epidural and intravenous (i.v.) oxycodone at the same dose.
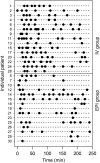
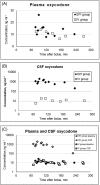
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind, double-dummy clinical trial, 30 women, aged 24-67 years, undergoing elective gynaecological laparotomy, were administrated either i.v. saline and epidural oxycodone 0.1 mg·kg-1 (EPI group; n = 15) or i.v. oxycodone 0.1 mg·kg-1 and epidural saline (IV group; n = 15). For multimodal analgesia, patients received i.v. paracetamol and dexketoprofen, and a triple-mixture epidural infusion after the first 4 h postoperatively. The primary outcome was the total dose of i.v. fentanyl for rescue analgesia during the first 4 h postoperatively.
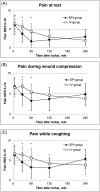
Results: All patients required fentanyl during the first 4 h. The median number of fentanyl doses were three (quartiles 1, 8) in the EPI group and seven (6, 9) in the IV group (mean difference 3.1; 95% confidence interval 0.9, 5.2; P = 0.01). After the first 4 h, the two groups needed a similar total dose of epidural infusion. Patient satisfaction was similarly high in both groups, and both administration routes were well tolerated.
Conclusions: The data support the superiority of epidural oxycodone compared with that of i.v. administration in pain management after laparotomy.
Keywords: analgesia; epidural; laparotomy; oxycodone.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Kokki H, Kokki M, Sjövall S. Oxycodone for the treatment of postoperative pain. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2012; 13: 1045–1058. - PubMed
-
- Kokki H, Rasanen I, Laisalmi M, Lehtola S, Ranta VP, Vanamo K, et al Comparison of oxycodone pharmacokinetics after buccal and sublingual administration in children. Clin Pharmacokinet 2006; 45: 745–754. - PubMed
-
- Olkkola KT, Kontinen VK, Saari TI, Kalso EA. Does the pharmacology of oxycodone justify its increasing use as an analgesic? Trends Pharmacol Sci 2013; 34: 206–214. - PubMed
-
- Kokki M, Välitalo P, Kuusisto M, Ranta VP, Raatikainen K, Hautajärvi H, et al Central nervous system penetration of oxycodone after intravenous and epidural administration. Br J Anaesth 2014; 112: 133–140. - PubMed
-
- Kalso E, Pöyhiä R, Onnela P, Linko K, Tigerstedt I, Tammisto T. Intravenous morphine and oxycodone for pain after abdominal surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1991; 35: 642–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

