Analysis of sulfates on low molecular weight heparin using mass spectrometry: structural characterization of enoxaparin
- PMID: 29782806
- PMCID: PMC10134193
- DOI: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1480110
Analysis of sulfates on low molecular weight heparin using mass spectrometry: structural characterization of enoxaparin
Abstract
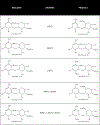
Structural characterization of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is critical to meet biosimilarity standards. In this context, the review focuses on structural analysis of labile sulfates attached to the side-groups of LMWH using mass spectrometry. A comprehensive review of this topic will help readers to identify key strategies for tackling the problem related to sulfate loss. At the same time, various mass spectrometry techniques are presented to facilitate compositional analysis of LMWH, mainly enoxaparin. Areas covered: This review summarizes findings on mass spectrometry application for LMWH, including modulation of sulfates, using enzymology and sample preparation approaches. Furthermore, popular open-source software packages for automated spectral data interpretation are also discussed. Successful use of LC/MS can decipher structural composition for LMWH and help evaluate their sameness or biosimilarity with the innovator molecule. Overall, the literature has been searched using PubMed by typing various search queries such as 'enoxaparin', 'mass spectrometry', 'low molecular weight heparin', 'structural characterization', etc. Expert commentary: This section highlights clinically relevant areas that need improvement to achieve satisfactory commercialization of LMWHs. It also primarily emphasizes the advancements in instrumentation related to mass spectrometry, and discusses building automated software for data interpretation and analysis.
Keywords: Low molecular weight heparin; enoxaparin; mass spectrometry; size exclusion chromatography; sulfolyltransferase.
Figures


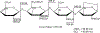
Similar articles
-
Fragment profiling of low molecular weight heparins using reversed phase ion pair liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry.Carbohydr Res. 2015 Apr 30;407:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Carbohydr Res. 2015. PMID: 25701653
-
Glycan Mapping of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Using Mass Spectral Correction Based on Chromatography Fitting with "Glycomapping" Software.Anal Chem. 2022 Sep 27;94(38):13000-13009. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01579. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 36102213
-
Liquid chromatography-diode array detection-mass spectrometry for compositional analysis of low molecular weight heparins.Anal Biochem. 2014 Apr 15;451:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.02.005. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Anal Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24530286
-
Differentiation of the low-molecular-weight heparins.Pharmacotherapy. 2001 Jun;21(6 Pt 2):62S-70S; discussion 71S-72S. doi: 10.1592/phco.21.8.62s.34594. Pharmacotherapy. 2001. PMID: 11401195 Review.
-
Combination of low molecular weight heparins with antiplatelet agents in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: an update.Drugs. 2002;62(12):1755-70. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262120-00005. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12149045 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanism of the Anti-Inflammatory Action of Heparin.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 3;22(19):10730. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910730. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639073 Free PMC article.
-
Release characteristics of enoxaparin sodium-loaded polymethylmethacrylate bone cement.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Feb 4;16(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02223-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 33541384 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Quantitative Methods & Modeling and Analytical Techniques in Reverse Engineering; A Cutting-Edge Strategy in Complex Generic Development.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Mar 26;26(4):92. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03067-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40140161 Review.
-
Biosimilars of low molecular weight heparins: Relevant background information for your drug formulary.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;85(11):2479-2486. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14081. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31378961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific Non-Reducing Ends in Heparins from Different Animal Origins: Building Blocks Analysis Using Reductive Amination Tagging by Sulfanilic Acid.Molecules. 2020 Nov 26;25(23):5553. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235553. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33256116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guerrini M, Bisio A, Low-molecular-weight heparins: differential characterization/physical characterization, Handb Exp Pharmacol (2012) 127–157. - PubMed
-
- Alam F, Hwang SR, Al-Hilal TA, et al., Safety studies on intravenous infusion of a potent angiogenesis inhibitor: taurocholate-conjugated low molecular weight heparin derivative LHT7 in preclinical models, Drug Dev Ind Pharm 42 (2016) 1247–1257. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar OM, Kleiman NS, Low molecular weight heparins, Expert Opin Pharmacother 1 (2000) 1091–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
