The impact of pharmacokinetic gene profiles across human cancers
- PMID: 29783934
- PMCID: PMC5963084
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4345-2
The impact of pharmacokinetic gene profiles across human cancers
Erratum in
-
Correction to: the impact of pharmacokinetic gene profiles across human cancers.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jul 18;18(1):743. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4593-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30021563 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The right drug to the right patient at the right time is one of the ideals of Individualized Medicine (IM) and remains one of the most compelling promises of the post-genomic age. The addition of genomic information is expected to increase the precision of an individual patient's treatment, resulting in improved outcomes. While pilot studies have been encouraging, key aspects of interpreting tumor genomics information, such as somatic activation of drug transport or metabolism, have not been systematically evaluated.
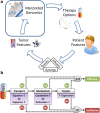
Methods: In this work, we developed a simple rule-based approach to classify the therapies administered to each patient from The Cancer Genome Atlas PanCancer dataset (n = 2858) as effective or ineffective. Our Therapy Efficacy model used each patient's drug target and pharmacokinetic (PK) gene expression profile; the specific genes considered for each patient depended on the therapies they received. Patients who received predictably ineffective therapies were considered at high-risk of cancer-related mortality and those who did not receive ineffective therapies were considered at low-risk. The utility of our Therapy Efficacy model was assessed using per-cancer and pan-cancer differential survival.
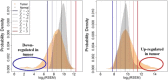
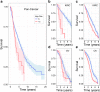
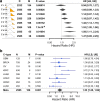
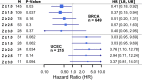
Results: Our simple rule-based Therapy Efficacy model classified 143 (5%) patients as high-risk. High-risk patients had age ranges comparable to low-risk patients of the same cancer type and tended to be later stage and higher grade (odds ratios of 1.6 and 1.4, respectively). A significant pan-cancer association was identified between predictions of our Therapy Efficacy model and poorer overall survival (hazard ratio, HR = 1.47, p = 6.3 × 10- 3). Individually, drug export (HR = 1.49, p = 4.70 × 10- 3) and drug metabolism (HR = 1.73, p = 9.30 × 10- 5) genes demonstrated significant survival associations. Survival associations for target gene expression are mechanism-dependent. Similar results were observed for event-free survival.
Conclusions: While the resolution of clinical information within the dataset is not ideal, and modeling the relative contribution of each gene to the activity of each therapy remains a challenge, our approach demonstrates that somatic PK alterations should be integrated into the interpretation of somatic transcriptomic profiles as they likely have a significant impact on the survival of specific patients. We believe that this approach will aid the prospective design of personalized therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Cancer treatment protocols; Genomic interpretation; Individualized medicine; Pharmacokinetics; Transcriptome profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The results shown here are based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network:
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Bielinski SJ, Olson JE, Pathak J, Weinshilboum RM, Wang L, Lyke KJ, Ryu E, Targonski PV, Van Norstrand MD, Hathcock MA, et al. Preemptive genotyping for personalized medicine: design of the right drug, right dose, right time-using genomic data to individualize treatment protocol. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.10.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson DB, Dahlman KH, Knol J, Gilbert J, Puzanov I, Means-Powell J, Balko JM, Lovly CM, Murphy BA, Goff LW, et al. Enabling a genetically informed approach to cancer medicine: a retrospective evaluation of the impact of comprehensive tumor profiling using a targeted next-generation sequencing panel. Oncologist. 2014;19(6):616–622. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

