A genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions and positional candidate genes for fat deposition in broiler chickens
- PMID: 29783939
- PMCID: PMC5963092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-4779-6
A genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions and positional candidate genes for fat deposition in broiler chickens
Abstract
Background: Excess fat content in chickens has a negative impact on poultry production. The discovery of QTL associated with fat deposition in the carcass allows the identification of positional candidate genes (PCGs) that might regulate fat deposition and be useful for selection against excess fat content in chicken's carcass. This study aimed to estimate genomic heritability coefficients and to identify QTLs and PCGs for abdominal fat (ABF) and skin (SKIN) traits in a broiler chicken population, originated from the White Plymouth Rock and White Cornish breeds.
Results: ABF and SKIN are moderately heritable traits in our broiler population with estimates ranging from 0.23 to 0.33. Using a high density SNP panel (355,027 informative SNPs), we detected nine unique QTLs that were associated with these fat traits. Among these, four QTL were novel, while five have been previously reported in the literature. Thirteen PCGs were identified that might regulate fat deposition in these QTL regions: JDP2, PLCG1, HNF4A, FITM2, ADIPOR1, PTPN11, MVK, APOA1, APOA4, APOA5, ENSGALG00000000477, ENSGALG00000000483, and ENSGALG00000005043. We used sequence information from founder animals to detect 4843 SNPs in the 13 PCGs. Among those, two were classified as potentially deleterious and two as high impact SNPs.
Conclusions: This study generated novel results that can contribute to a better understanding of fat deposition in chickens. The use of high density array of SNPs increases genome coverage and improves QTL resolution than would have been achieved with low density. The identified PCGs were involved in many biological processes that regulate lipid storage. The SNPs identified in the PCGs, especially those predicted as potentially deleterious and high impact, may affect fat deposition. Validation should be undertaken before using these SNPs for selection against carcass fat accumulation and to improve feed efficiency in broiler chicken production.
Keywords: Abdominal fat; Fatness; Genomic heritability; QTL; Skin weight.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All experimental protocols related to animal experimentation in this study were performed in agreement with the resolution number 010/2012 approved by the Embrapa Swine and Poultry Ethics Committee on Animal Utilization to ensure compliance with international guidelines for animal welfare.
Competing interests
Dr. James Reecy is a member of the editorial board (Associate Editor) of BMC Genetics journal.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
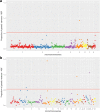
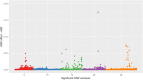

References
-
- Resnky CW, Carré W, Wang X, Porter TE, Simon J, Le Bihan-Duval E, et al. Transcriptional analysis of abdominal fat in genetically fat and lean chickens reveals adipokines, lipogenic genes and a link between hemostasis and leanness. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:557. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-557. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nassar MK, Goraga ZS, Brockmann G. Quantitative trait loci segregating in crosses between New Hampshire and white leghorn chicken lines: III. Fat deposition and intramuscular fat content. Anim Genet. 2012;1(44):62–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2014/08704-0/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2014/21380-9/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2016/00569-1/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2015/00616-7/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 370620/2013-5/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

