Small RNA-based prediction of hybrid performance in maize
- PMID: 29783940
- PMCID: PMC5963143
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-4708-8
Small RNA-based prediction of hybrid performance in maize
Abstract
Background: Small RNA (sRNA) sequences are known to have a broad impact on gene regulation by various mechanisms. Their performance for the prediction of hybrid traits has not yet been analyzed. Our objective was to analyze the relation of parental sRNA expression with the performance of their hybrids, to develop a sRNA-based prediction approach, and to compare it to more common SNP and mRNA transcript based predictions using a factorial mating scheme of a maize hybrid breeding program.
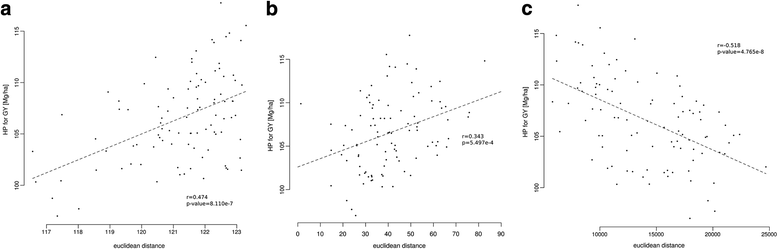
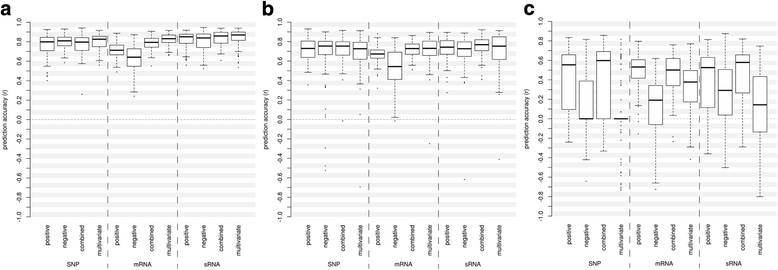
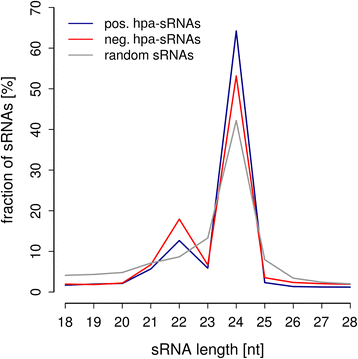
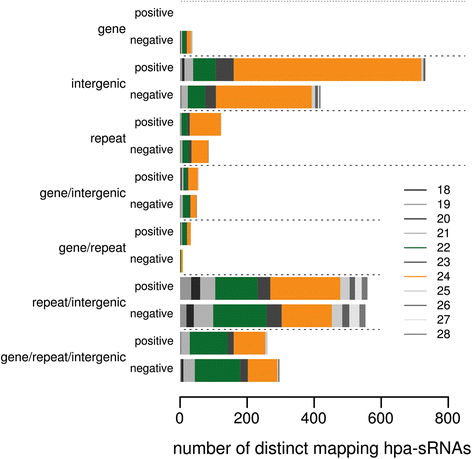
Results: Correlation of genomic differences and messenger RNA (mRNA) or sRNA expression differences between parental lines with hybrid performance of their hybrids revealed that sRNAs showed an inverse relationship in contrast to the other two data types. We associated differences for SNPs, mRNA and sRNA expression between parental inbred lines with the performance of their hybrid combinations and developed two prediction approaches using distance measures based on associated markers. Cross-validations revealed parental differences in sRNA expression to be strong predictors for hybrid performance for grain yield in maize, comparable to genomic and mRNA data. The integration of both positively and negatively associated markers in the prediction approaches enhanced the prediction accurary. The associated sRNAs belong predominantly to the canonical size classes of 22- and 24-nt that show specific genomic mapping characteristics.
Conclusion: Expression profiles of sRNA are a promising alternative to SNPs or mRNA expression profiles for hybrid prediction, especially for plant species without reference genome or transcriptome information. The characteristics of the sRNAs we identified suggest that association studies based on breeding populations facilitate the identification of sRNAs involved in hybrid performance.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Grain yield; Hybrid performance; Hybrid trait prediction; Maize; SNP; Small RNA; Transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The plant material used in this study was developed and tested within the maize breeding program of the University of Hohenheim. The experiments comply with the institutional and national guidelines in Germany.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Melchinger AE. Genetic diversity and heterosis. In: Coors JG, Pandey S, editors. The genetics and exploitation of heterosis in crops. Madison: ASA-CSSA; 1999. pp. 99–118.
-
- Schrag TA, Möhring J, Maurer HP, Dhillon BS, Melchinger AE, Piepho HP, Sørensen AP, Frisch M. Molecular marker-based prediction of hybrid performance in maize using unbalanced data from multiple experiments with factorial crosses. Theor Appl Genet. 2009;118:741–751. doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0934-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

