Adding colchicine to immunosuppressive treatments; a potential option for biologics-refractory adult-onset Still's disease
- PMID: 29784018
- PMCID: PMC5963072
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3420-8
Adding colchicine to immunosuppressive treatments; a potential option for biologics-refractory adult-onset Still's disease
Abstract
Background: Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a rare inflammatory disorder characterized by the classical triad of daily spiking fever, arthritis, and typical salmon-colored rash. Resistance to first-line corticosteroids and second-line disease modified anti-rheumatic-drugs defines refractory AOSD, which mostly includes the polycyclic or chronic courses of the disease. Anti-cytokine therapies are recommended in AOSD patients who are refractory to traditional treatments. This is the first report on the efficacy of colchicine in a patient with AOSD which was refractory to immunosuppressive treatments including biologics.
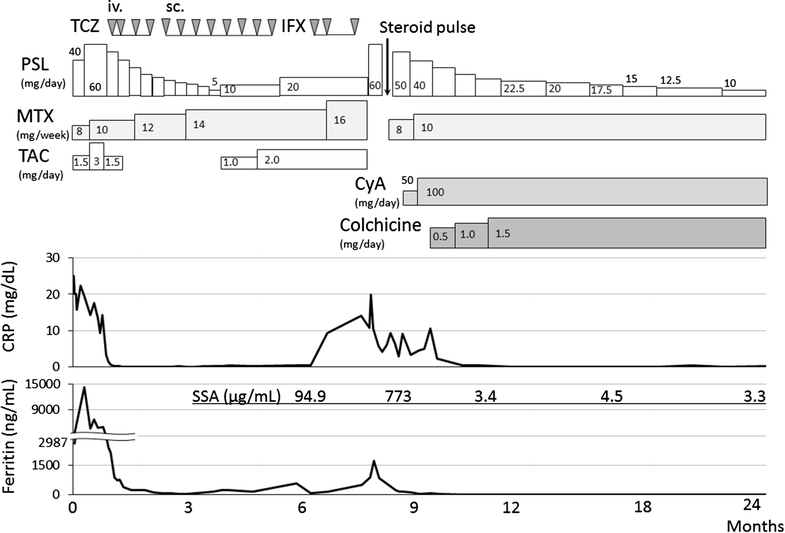
Case presentation: A 24-years Japanese female patient was referred to our hospital for the flare-up of AOSD under the combined treatments with steroid, immunosuppressants, and biologics. She was diagnosed with AOSD according to the Yamaguchi criteria, based on the presence of spiking fever, polyarthralgia, skin rash, and hyperferritinemia. Interleukin-6 or tumor necrosis factor-α blockade treatments were not effective, the oral administration of colchicine was stared under the immunosuppressive treatments with steroid and cyclosporine A (CyA). Colchicine treatment silenced the disease activity of AOSD. The dose of prednisolone was successfully tapered, and the elevated levels of C-reactive protein were normalized. Remission has been maintained for 13 months with the start of oral administration of colchicine.
Conclusion: We concluded that colchicine is an alternative treatment in patients with refractory AOSD, particularly in those with impaired therapeutic effects against anti-cytokines therapies.
Keywords: Adult-onset Still’s disease; Colchicine; Cyclosporin A; Tocilizumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis and management of adult-onset Still's disease.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Dec;36(3):144-52. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.07.001. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16949136 Review.
-
Urticarial rash, fever, and arthritis: A case of refractory Adult-onset Still's disease with good response to tocilizumab.Dermatol Ther. 2019 Sep;32(5):e13041. doi: 10.1111/dth.13041. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Dermatol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31361930 Review.
-
Leukocytapheresis (LCAP) for treating refractory adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD).Mod Rheumatol. 2012 Jun;22(3):483-7. doi: 10.1007/s10165-011-0543-3. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Mod Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22020671
-
Adult-onset Still's disease in focus: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and unmet needs in the era of targeted therapies.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021 Aug;51(4):858-874. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jun 13. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021. PMID: 34175791 Review.
-
Adult-onset Still's disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation and hemophagocytic syndrome: a case report.BMC Res Notes. 2014 Dec 22;7:940. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-940. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 25532568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A case of adult-onset Still's disease accompanied with pulmonary tuberculosis successfully treated with colchicine.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021 Oct;38(5):912-915. doi: 10.5114/ada.2021.110105. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021. PMID: 34849145 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adult-onset Still's disease: A disease at the crossroad of innate immunity and autoimmunity.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 22;9:881431. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.881431. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36072947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refractory adult-onset Still's disease complicated with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32107. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032107. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626532 Free PMC article.
-
An undiagnosed patient with skin rash, polyarthritis, and edema responding to low-dose colchicine: A case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021 Jun 12;9:2050313X211024508. doi: 10.1177/2050313X211024508. eCollection 2021. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34178350 Free PMC article.
-
An adult case of atypical familial Mediterranean fever (pyrin-associated autoinflammatory disease) similar to adult-onset Still's disease.Clin Case Rep. 2019 Mar 12;7(4):801-805. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2102. eCollection 2019 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30997089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials