Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer
- PMID: 29784041
- PMCID: PMC5993136
- DOI: 10.1186/s40880-018-0301-4
Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer
Abstract
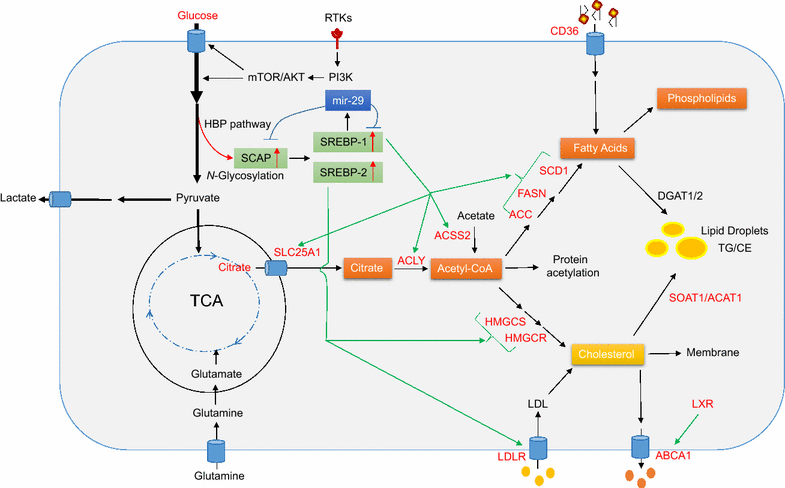
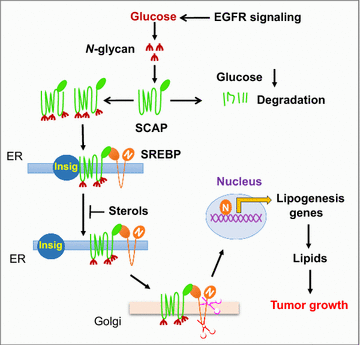
Reprogramming of lipid metabolism is a newly recognized hallmark of malignancy. Increased lipid uptake, storage and lipogenesis occur in a variety of cancers and contribute to rapid tumor growth. Lipids constitute the basic structure of membranes and also function as signaling molecules and energy sources. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs), a family of membrane-bound transcription factors in the endoplasmic reticulum, play a central role in the regulation of lipid metabolism. Recent studies have revealed that SREBPs are highly up-regulated in various cancers and promote tumor growth. SREBP cleavage-activating protein is a key transporter in the trafficking and activation of SREBPs as well as a critical glucose sensor, thus linking glucose metabolism and de novo lipid synthesis. Targeting altered lipid metabolic pathways has become a promising anti-cancer strategy. This review summarizes recent progress in our understanding of lipid metabolism regulation in malignancy, and highlights potential molecular targets and their inhibitors for cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; Cholesterol; Fatty acids; Lipid droplets; Lipid metabolism; SCAP; SREBPs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

