Interactions between kappa and mu opioid receptor agonists: effects of the ratio of drugs in mixtures
- PMID: 29785554
- PMCID: PMC6045970
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-4920-x
Interactions between kappa and mu opioid receptor agonists: effects of the ratio of drugs in mixtures
Abstract
Rationale: Pain is the leading reason for seeking health care, and mu opioid receptor agonists continue to be prescribed despite well-documented adverse effects. Kappa opioid receptor agonists have antinociceptive effects with little to no abuse liability and might be useful for treating pain in mixtures. Kappa:mu opioid mixtures might be useful if therapeutic effects of each drug can be selectively increased while reducing or avoiding the adverse effects that occur with larger doses of each drug alone.
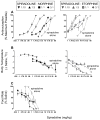
Objective: This study characterized the effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist spiradoline alone (0.32-56 mg/kg) and in 1:10, 1:3, 1:1, and 3:1 mixtures with the mu opioid receptor agonists morphine (1.0-32 mg/kg) and etorphine (1-10 μg/kg) on warm water tail-withdrawal latency, body temperature, responding for food, and fecal output in male Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 24).
Results: Antinociceptive effects were greater than additive for 1:10 and 1:3 spiradoline:morphine mixtures and for 1:10, 1:3, and 1:1 spiradoline:etorphine mixtures. The potency of spiradoline to produce hypothermia was greater with 1:3 and 3:1 spiradoline:etorphine mixtures but not with 1:10 or 1:1 mixtures or with any spiradoline:morphine mixture. The effects of 1:3 spiradoline:morphine on responding for food were additive, whereas 1:1 and 3:1 were greater than additive. Spiradoline did not significantly alter morphine-induced decreases in fecal output.
Conclusions: Overall, mixtures of kappa and mu opioids might have therapeutic potential for treating pain, particularly when the mixture has a greater ratio of mu to kappa agonist. If adverse effects of each constituent drug are reduced or avoided, then kappa:mu mixtures might be advantageous to mu opioids alone.
Keywords: Antinociception; Drug interactions; Drug mixtures; Opioids; Rats.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has a conflict to declare
Figures



Similar articles
-
Behavioral Characterization of κ Opioid Receptor Agonist Spiradoline and Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist CP55940 Mixtures in Rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Feb;360(2):280-287. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.235630. Epub 2016 Nov 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 27903642 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ blocks the antinociception induced by mu, kappa and delta opioid agonists on the cold water tail-flick test.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Feb 14;557(1):32-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.11.001. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17173891 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic sucrose intake augments antinociception induced by injections of mu but not kappa opioid receptor agonists into the periaqueductal gray matter in male and female rats.Brain Res. 2001 Nov 30;920(1-2):97-105. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03039-6. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11716815
-
Biased Opioid Ligands.Molecules. 2020 Sep 16;25(18):4257. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184257. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32948048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kappa and Mu Opioid Receptors in Chronic Cough: Current Evidence and Future Treatment.Lung. 2025 May 13;203(1):62. doi: 10.1007/s00408-025-00812-8. Lung. 2025. PMID: 40358749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of opioid/cannabinoid mixtures on impulsivity and memory in rhesus monkeys.Behav Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;31(2&3):233-248. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000551. Behav Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32101988 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of observable behaviors induced by typical and atypical kappa-opioid receptor agonists in male rhesus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Jul;237(7):2075-2087. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05519-7. Epub 2020 May 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32372348 Free PMC article.
-
The kappa-opioid receptor agonist, triazole 1.1, reduces oxycodone self-administration and enhances oxycodone-induced thermal antinociception in male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Dec;238(12):3463-3476. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05965-x. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34430992 Free PMC article.
-
Psychotropic Drugs for the Management of Chronic Pain and Itch.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Jun 24;12(2):99. doi: 10.3390/ph12020099. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31238561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Eating a Traditional High Fat/High Carbohydrate or a Ketogenic Diet on Sensitivity of Female Rats to Morphine.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Sep 18;391(1):30-38. doi: 10.1124/jpet.124.002188. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024. PMID: 39060162
References
-
- Briggs SL, Rech RH, Sawyer Kappa antinociceptive activity of spiradoline in the cold-water tail-flick assay in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998;60:467–472. - PubMed
-
- Binder W, Carmody J, Walker J. Effect of gender on anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions of two k-opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;292:303–309. - PubMed
-
- Dart RC, Surratt HL, Cicero TJ, Parrino MW, Severtson SG, Bucher-Bartelson B, Green JL. Trends in opioid analgesia abuse and mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Dosaka-Akita K, Tortella FC, Holaday JW, Long JB. The kappa opioid agonist U-50,488H antagonizes respiratory effects of mu opioid receptor agonists in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:631–637. - PubMed
-
- Dykstra LA, Gmerek DE, Winger G, Woods JE. Kappa opioids in rhesus monkeys. I. Diuresis, sedations, analgesia, and discriminative stimulus effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;242:413–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

