Body Composition Profiling in the UK Biobank Imaging Study
- PMID: 29785727
- PMCID: PMC6220857
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.22210
Body Composition Profiling in the UK Biobank Imaging Study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of imaging-based multivariable body composition profiling by describing its association with coronary heart disease (CHD), type 2 diabetes (T2D), and metabolic health on individual and population levels.
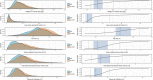
Methods: The first 6,021 participants scanned by UK Biobank were included. Body composition profiles (BCPs) were calculated, including abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue, visceral adipose tissue (VAT), thigh muscle volume, liver fat, and muscle fat infiltration (MFI), determined using magnetic resonance imaging. Associations between BCP and metabolic status were investigated using matching procedures and multivariable statistical modeling.
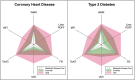
Results: Matched control analysis showed that higher VAT and MFI were associated with CHD and T2D (P < 0.001). Higher liver fat was associated with T2D (P < 0.001) and lower liver fat with CHD (P < 0.05), matching on VAT. Multivariable modeling showed that lower VAT and MFI were associated with metabolic health (P < 0.001), and liver fat was nonsignificant. Associations remained significant adjusting for sex, age, BMI, alcohol, smoking, and physical activity.
Conclusions: Body composition profiling enabled an intuitive visualization of body composition and showed the complexity of associations between fat distribution and metabolic status, stressing the importance of a multivariable approach. Different diseases were linked to different BCPs, which could not be described by a single fat compartment alone.
© 2018 The Authors. Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Obesity Society (TOS).
Figures



References
-
- Prentice AM, Jebb SA. Beyond body mass index. Obes Rev 2001;2:141‐147. - PubMed
-
- Tomiyama AJ, Hunger JM, Nguyen‐Cuu J, Wells C. Misclassification of cardiometabolic health when using body mass index categories in NHANES 2005‐20112. Int J Obes (Lond) 2016;40:883‐886. - PubMed
-
- Thomas EL, Fitzpatrick JA, Malik SJ, Taylor‐Robinson SD, Bell JD. Whole body fat: content and distribution. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 2013;73:56‐80. - PubMed
-
- Schlett CL, Hendel T, Weckbach S, et al. Population‐based imaging and radiomics: rationale and perspective of the German National Cohort MRI Study. Rofo 2016;188:652‐661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

