Role of Soluble ST2 Levels and Beta-Blockers Dosage on Cardiovascular Events of Patients with Unselected ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 29786039
- PMCID: PMC5987497
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.232819
Role of Soluble ST2 Levels and Beta-Blockers Dosage on Cardiovascular Events of Patients with Unselected ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Serum soluble ST2 (sST2) levels are elevated early after acute myocardial infarction and are related to adverse left ventricular (LV) remodeling and cardiovascular outcomes in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Beta-blockers (BB) have been shown to improve LV remodeling and survival. However, the relationship between sST2, final therapeutic BB dose, and cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients remains unknown.
Methods: A total of 186 STEMI patients were enrolled at the Wuhan Asia Heart Hospital between January 2015 and June 2015. All patients received standard treatment and were followed up for 1 year. Serum sST2 was measured at baseline. Patients were divided into four groups according to their baseline sST2 values (high >56 ng/ml vs. low ≤56 ng/ml) and final therapeutic BB dose (high ≥47.5 mg/d vs. low <47.5 mg/d). Cox regression analyses were performed to determine whether sST2 and BB were independent risk factors for cardiovascular events in STEMI.
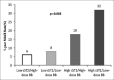
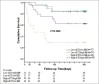
Results: Baseline sST2 levels were positively correlated with heart rate (r = 0.327, P = 0.002), Killip class (r = 0.408, P = 0.000), lg N-terminal prohormone B-type natriuretic peptide (r = 0.467, P = 0.000), lg troponin I (r = 0.331, P = 0.000), and lg C-reactive protein (r = 0.307, P = 0.000) and negatively correlated to systolic blood pressure (r = -0.243, P = 0.009) and LV ejection fraction (r = -0.402, P = 0.000). Patients with higher baseline sST2 concentrations who were not titrated to high-dose BB therapy (P < 0.0001) had worse outcomes. Baseline high sST2 (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.653; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.201-8.929; P = 0.041) and final low BB dosage (HR: 1.904; 95% CI, 1.084-3.053; P = 0.035) were independent predictors of cardiovascular events in STEMI.
Conclusions: High baseline sST2 levels and final low BB dosage predicted cardiovascular events in STEMI. Hence, sST2 may be a useful biomarker in cardiac pathophysiology.
血清可溶性ST2水平、β受体阻滞剂治疗与ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者预后的关系摘要背景: 有研究发现血清可溶性ST2(sST2)水平在急性心肌梗死发生早期升高,同时与ST段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)患者的左心室重构及预后相关。β受体阻滞剂通过改善STEMI患者左心室重构进而改善预后。本研究初步探讨了STEMI患者中基线sST2水平,β受体阻滞剂剂量与预后的关系。 方法: 2015年1月至6月于武汉亚洲心脏病医院纳入符合标准的186名STEMI患者。所有患者接受正规治疗并随访至1年。测量患者基线血清sST2水平。依据基线sST2水平(高sST2>56 ng/ml vs. 低sST2 ≤56 ng/ml)及最终β受体阻滞剂的治疗剂量(高剂量组≥47.5mg vs. 低剂量组 <47.5)分为4组。应用 Cox 回归分析确定sST2水平 、BB剂量在STEMI患者中的预测价值。 结果: 基线sST2水平与心率(r=0.327, p=0.002)、Killip class (r=0.408,p=0.000), lgNTproBNP (r=0.467, p=0.000), lgTnI (r=0.331, p=0.000) 和 lgCRP (r=0.307, p=0.000)正相关,与SBP (r=-0.243,p=0.009) 和 LVEF (r=-0.402, p=0.000)负相关。基线sST2升高伴低剂量BB的患者预后较差(p=0.000)。基线高sST2水平 (HR, 2.653; 95% CI, 1.201-8.929; p=0.041) 及低剂量BB (HR, 1.904; 95% CI, 1.084-3.053; p=0.035) 是STEMI患者出现心血管事件的独立预测因素。 结论: 基线高sST2水平及低剂量BB是STEMI患者出现心血管事件的独立预测因素, sST2 可能是心脏病理生理过程的一个有用生物标记物。.
Keywords: Adrenergic Beta-Antagonists; Prognosis; ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction; ST2.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term prognostic importance of high levels of sST2 in patient with AMI: a meta-analysis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jan 15;16(1):1-11. doi: 10.62347/HAQL3794. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38322566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble concentrations of the interleukin receptor family member ST2 and β-blocker therapy in chronic heart failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2013 Nov;6(6):1206-13. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.113.000457. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Circ Heart Fail. 2013. PMID: 24114865 Clinical Trial.
-
Short-term predictive value of sST2 in patients with STEMI following primary PCI: a prospective observational study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Jan 15;25(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04488-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 39819309 Free PMC article.
-
Improved early risk stratification of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention using a combination of serum soluble ST2 and NT-proBNP.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 10;12(8):e0182829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182829. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28796845 Free PMC article.
-
Does Oral Beta-Blocker Therapy Improve Long-Term Survival in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Preserved Systolic Function? A Meta-Analysis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016 May;21(3):280-5. doi: 10.1177/1074248415608011. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26424094 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term prognostic importance of high levels of sST2 in patient with AMI: a meta-analysis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jan 15;16(1):1-11. doi: 10.62347/HAQL3794. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38322566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of β-Blocker Therapy on the Level of Soluble ST2 Protein in Pediatric Dilated Cardiomyopathy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Sep 23;58(10):1339. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101339. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295500 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term and long-term prognostic value of circulating soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 concentration in acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 4;39(6):BSR20182441. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182441. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31092701 Free PMC article.
-
The association between soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 and long-term prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 4;15(9):e0238775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238775. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32886697 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 associated with left ventricular thrombosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Mar 20;25(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04667-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40114062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tominaga Si, Kuroiwa K, Tago K, Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Komatsu N, et al. Presence and expression of a novel variant form of ST2 gene product in human leukemic cell line UT-7/GM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;264:14–8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1469. - PubMed
-
- Shimpo M, Morrow DA, Weinberg EO, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Antman EM, et al. Serum levels of the interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2 predict mortality and clinical outcome in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109:2186–90. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000127958.21003.5A. - PubMed
-
- Weir RA, Miller AM, Murphy GE, Clements S, Steedman T, Connell JM, et al. Serum soluble ST2: A potential novel mediator in left ventricular and infarct remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:243–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc. 2009.08.047. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials