Plasma Membrane Localization of Apoptotic Caspases for Non-apoptotic Functions
- PMID: 29787709
- PMCID: PMC5972739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.04.020
Plasma Membrane Localization of Apoptotic Caspases for Non-apoptotic Functions
Abstract
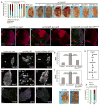
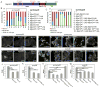
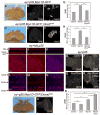
Caspases are best characterized for their function in apoptosis. However, they also have non-apoptotic functions such as apoptosis-induced proliferation (AiP), where caspases release mitogens for compensatory proliferation independently of their apoptotic role. Here, we report that the unconventional myosin, Myo1D, which is known for its involvement in left/right development, is an important mediator of AiP in Drosophila. Mechanistically, Myo1D translocates the initiator caspase Dronc to the basal side of the plasma membrane of epithelial cells where Dronc promotes the activation of the NADPH-oxidase Duox for reactive oxygen species generation and AiP in a non-apoptotic manner. We propose that the basal side of the plasma membrane constitutes a non-apoptotic compartment for caspases. Finally, Myo1D promotes tumor growth and invasiveness of the neoplastic scrib RasV12 model. Together, we identified a new function of Myo1D for AiP and tumorigenesis, and reveal a mechanism by which cells sequester apoptotic caspases in a non-apoptotic compartment at the plasma membrane.
Keywords: Dronc; Drosophila; Myo1D; apoptosis-induced proliferation; non-apoptotic functions; plasma membrane.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Andrew DJ, Henderson KD, Seshaiah P. Salivary gland development in Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Dev. 2000;92:5–17. - PubMed
-
- Aram L, Braun T, Braverman C, Kaplan Y, Ravid L, Levin-Zaidman S, Arama E. A Krebs Cycle Component Limits Caspase Activation Rate through Mitochondrial Surface Restriction of CRL Activation. Developmental cell. 2016;37:15–33. - PubMed
-
- Barylko B, Binns DD, Albanesi JP. Regulation of the enzymatic and motor activities of myosin I. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 2000;1496:23–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

