Progression of Mineral Ion Abnormalities in Patients With Jansen Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia
- PMID: 29788189
- PMCID: PMC6486824
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-00332
Progression of Mineral Ion Abnormalities in Patients With Jansen Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia
Abstract
Context: Five different activating PTH/PTH-related peptide (PTHrP) receptor (PTHR1) mutations have been reported as causes of Jansen metaphyseal chondrodysplasia (JMC), a rare disorder characterized by severe growth plate abnormalities and PTH-independent hypercalcemia.
Objectives: Assess the natural history of clinical and laboratory findings in 24 patients with JMC and characterize the disease-causing mutant receptors in vitro.
Patients and methods: The H223R mutation occurred in 18 patients. T410P, I458R and I458K each occurred in single cases; T410R was present in a father and his two sons. Laboratory records were analyzed individually and in aggregate.
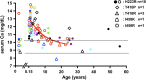
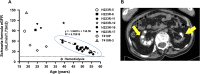
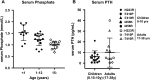
Results: Postnatal calcium levels were normal in most patients, but elevated between 0.15 and 10 years (11.8 ± 1.37 mg/dL) and tended to normalize in adults (10.0 ± 1.03 mg/dL). Mean phosphate levels were at the lower end of the age-specific normal ranges. Urinary calcium/creatinine (mg/mg) were consistently elevated (children, 0.80 ± 0.40; adults, 0.28 ± 0.19). Adult heights were well below the 3rd percentile for all patients, except for those with the T410R mutation. Most patients with JMC had undergone orthopedic surgical procedures, most had nephrocalcinosis, and two had advanced chronic kidney disease. The five PTHR1 mutants showed varying degrees of constitutive and PTH-stimulated cAMP signaling activity when expressed in HEK293 reporter cells. The inverse agonist [L11,dW12,W23,Y36]PTHrP(7-36) reduced basal cAMP signaling for each PTHR1 mutant.
Conclusions: Except for T410R, the other PTHR1 mutations were associated with indistinguishable mineral ion abnormalities and cause similarly severe growth impairment. Hypercalciuria persisted into adulthood. An inverse agonist ligand effectively reduced in vitro PTH-independent cAMP formation at all five PTHR1 mutants, suggesting a potential path toward therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Lee K, Deeds JD, Segre GV. Expression of parathyroid hormone-related peptide and its receptor messenger ribonucleic acids during fetal development of rats. Endocrinology. 1995;136(2):453–463. - PubMed
-
- Maes C, Kronenberg HM. Bone development and remodeling In: DeGroot LJ and Jameson JL, eds. Endocrinology. 7th ed.Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders; 2016:1038–1062.
-
- Gardella TJ, Jüppner H, Brown EM, Kronenberg HM, Potts JT Jr. Parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone receptor type 1 in the regulation of calcium and phosphate homeostasis and bone metabolism In: DeGroot LJ and Jameson JL, eds. Endocrinology. 7th ed.Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders; 2016:969–990.
-
- Jansen M. Über atypische Chondrodystrophie (Achondroplasie) und über eine noch nicht beschriebene angeborene Wachstumsstörung des Knochensystems: Metaphysäre Dysostosis. Zeitschr Orthop Chir. 1934;61:253–286.
-
- Schipani E, Kruse K, Jüppner H. A constitutively active mutant PTH-PTHrP receptor in Jansen-type metaphyseal chondrodysplasia. Science. 1995;268(5207):98–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

