Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation identified in plasma indicates failure sites and predicts clinical prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer progression during first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 29789021
- PMCID: PMC5993134
- DOI: 10.1186/s40880-018-0303-2
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation identified in plasma indicates failure sites and predicts clinical prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer progression during first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is an ideal approach to detecting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation, which is a major mechanism of resistance to first-generation EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy. The present study aimed to explore the association of ctDNA-identified T790M mutation with disease failure sites and clinical prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
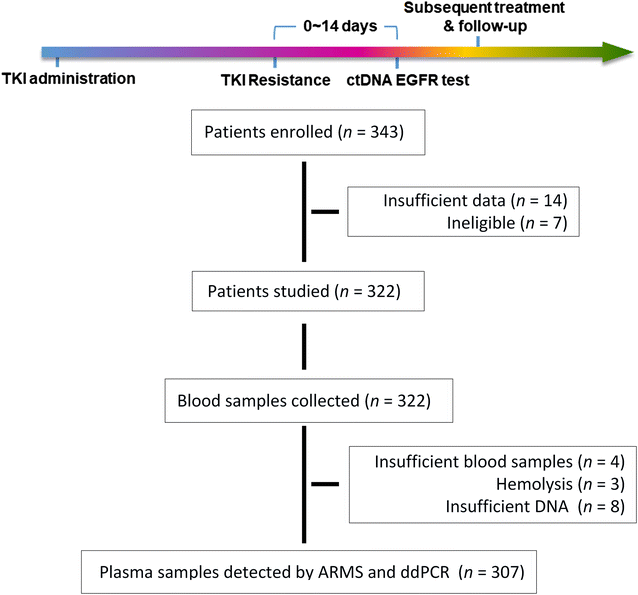
Methods: Patients who progressed on first-generation TKIs were categorized into failure site groups of chest limited (CF), brain limited (BF) and other (OF). Amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) were used to identify the T790M mutation in ctDNA. Prognosis was analyzed with Kaplan-Meier methods.
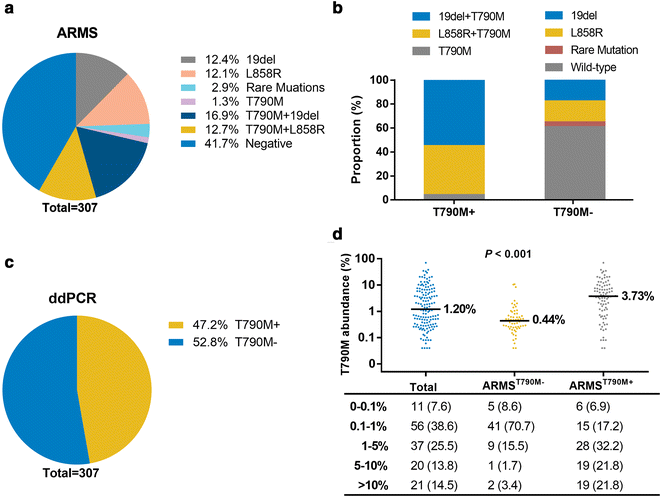
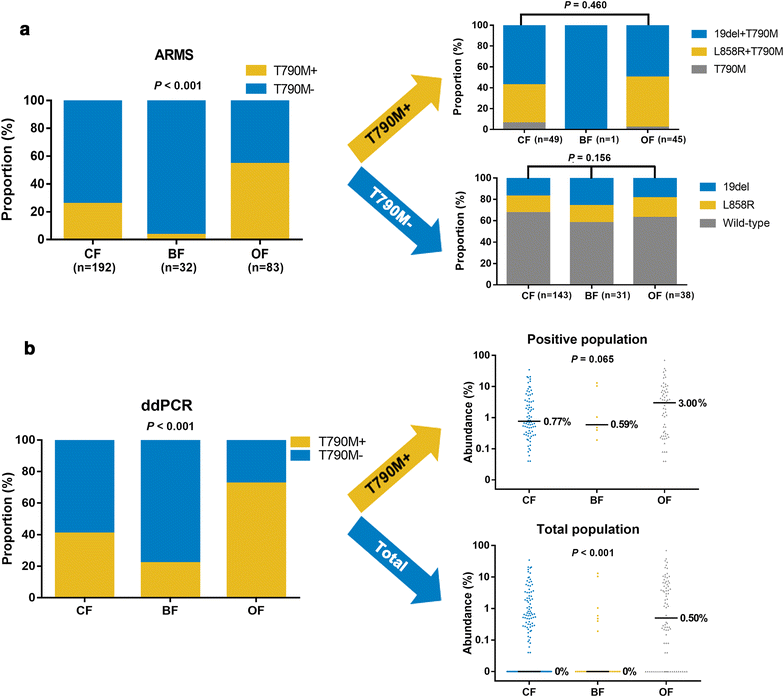
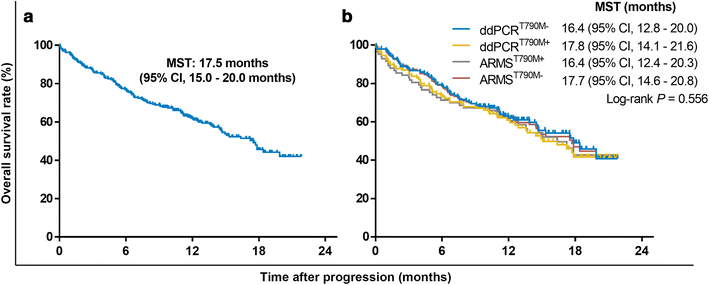
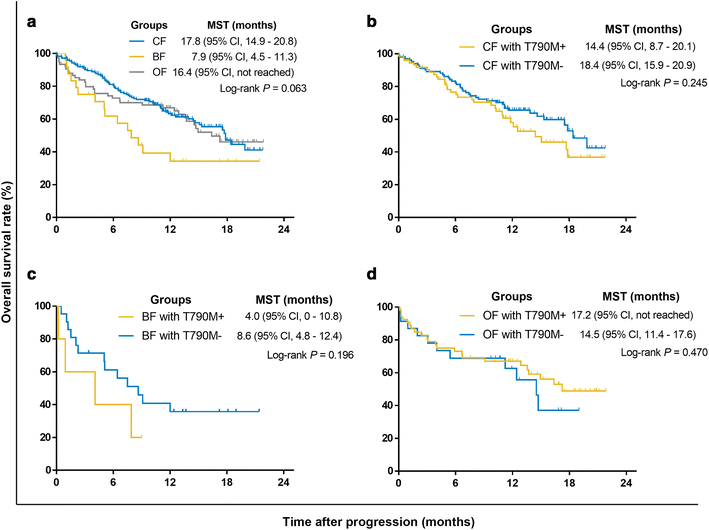
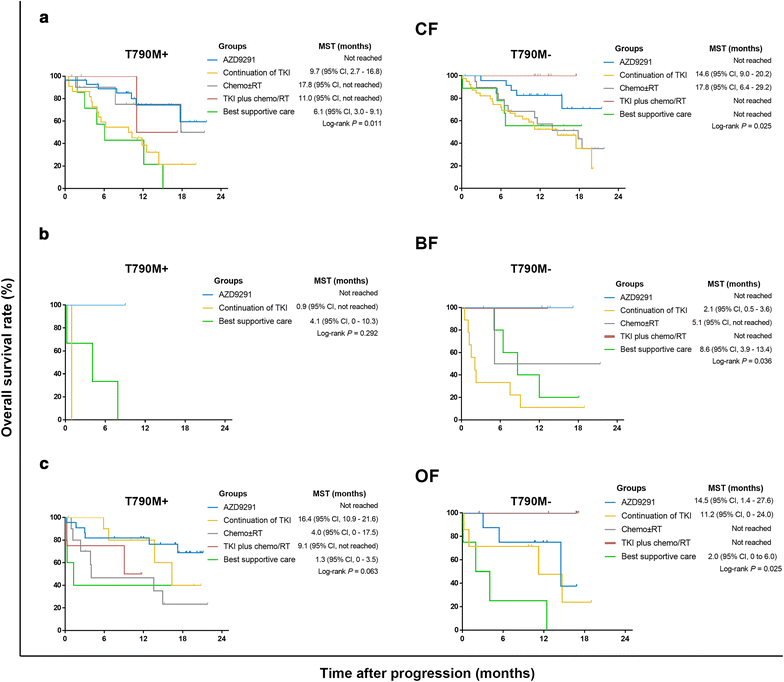
Results: Overall concordance between the two methods was 78.3%. According to both ARMS and ddPCR, patients in the OF group had a significantly higher rate of T790M mutation than did patients in the BF and CF groups (P < 0.001), and a significantly higher T790M mutation rate was also observed in OF-group patients than in those in the CF and BF groups (P < 0.001). AZD9291 was found to be an excellent treatment option and yielded the longest survival for T790M+ patients in all groups who had progressed on EGFR-TKIs; for other treatments, the prognosis of T790M- patient subgroups varied.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates that T790M mutation in ctDNA is associated with failure sites for NSCLC patients after EGFR-TKI therapy and indicates that both failure site and T790M mutational status greatly influence treatment selection and prognosis.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Failure sites; Non-small cell lung cancer; T790M; ctDNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) for the treatment of people with resected stage I to III non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR mutation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 27;5(5):CD015140. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015140.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40421698 Review.
-
Molecular testing, treatment patterns, and outcomes in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: the PISCES study.Future Oncol. 2025 Aug;21(19):2537-2547. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2025.2529094. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40717496
-
Real-world efficacy of osimertinib in previously EGFR-TKI treated NSCLC patients without identification of T790M mutation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Aug;148(8):2099-2114. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03766-5. Epub 2021 Aug 26. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34436667 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-specific efficacy of osimertinib in treatment-naïve EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer according to baseline genetic alterations in circulating tumor DNA.Invest New Drugs. 2025 Feb;43(1):101-107. doi: 10.1007/s10637-024-01500-9. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Invest New Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39789369
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TK) mutation testing in adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2014 May;18(32):1-166. doi: 10.3310/hta18320. Health Technol Assess. 2014. PMID: 24827857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Cancer Biomarkers: Oncogenic Mutations, Tissue and Liquid Biopsies, and Radiomics-A Review.Dig Dis Sci. 2023 Jul;68(7):2811-2823. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-07904-6. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Dig Dis Sci. 2023. PMID: 36988759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of somatic copy number variations in plasma cell free DNA correlating with intrinsic resistances to EGFR targeted therapy in T790M negative non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Mar;12(3):883-892. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.12.97. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32274156 Free PMC article.
-
Final report on plasma ctDNA T790M monitoring during EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer (JP-CLEAR trial).Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jul 8;52(7):791-794. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyac032. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35323965 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation pneumonitis after concurrent aumolertinib and thoracic radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;24(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11946-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38347438 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic recurrence risk and adjuvant chemotherapy benefit prediction by ctDNA in resected NSCLC.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 19;12(1):6770. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27022-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34799585 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

