MAP kinase signalling: interplays between plant PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity
- PMID: 29789867
- PMCID: PMC11105241
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-018-2839-3
MAP kinase signalling: interplays between plant PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity
Abstract
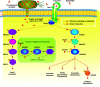
In plants, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are involved in regulating many biological processes including immunity. They relay signals from membrane-residing immune receptors to downstream components for defense activation. Arabidopsis MPK3/6 and MPK4 are activated in two parallel MAPK cascades during PAMP-triggered immunity. MPK3/6 have been implicated in the activation of various immune responses and their inactivation leads to compromised defense against pathogens. On the other hand, the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 cascade plays critical roles in basal resistance. Disruption of this MAPK cascade results in constitutive defense responses mediated by the NB-LRR protein SUMM2. Interestingly, SUMM2 guards the MEKK1-MKK1/2-MPK4 cascade activity indirectly through monitoring the phosphorylation status of CRCK3, which is a substrate of MPK4. From the pathogens' side, a number of effectors are shown to target various components of MAPK cascades in plants. Inactivation of MPK4 by the Pseudomonas effector HopAI1 triggers SUMM2-mediated immunity. Together, these findings suggest intricate interplays between PAMP-triggered immunity and effector-triggered immunity via MAPK signaling.
Keywords: CRCK3; Effector-triggered immunity; MAPK cascade; MPK3; MPK4; MPK6; Mitogen-activated protein kinases; PAMP-triggered immunity; SUMM2.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

