Potential pathogenicity of Inquilinus limosus in a pediatric patient with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 29790674
- PMCID: PMC6219391
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.24043
Potential pathogenicity of Inquilinus limosus in a pediatric patient with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
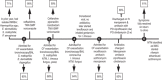
Presentation: Patient is a 6-year-old male with CF, MRSA colonization, and pancreatic insufficiency that presented with worsening ppFEV1 and systemic symptoms despite multiple interventions. BAL grew NTM, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Inquilinus limosus, a rare organism found in patients with CF.
Course: I. limosus treatment was deferred. Despite treatment of other pathogens, symptoms worsened. I. limosus was targeted with meropenem, amikacin, and ciprofloxacin along with clindamycin for MRSA colonization. Within weeks, symptoms had resolved with ppFEV1 improvement.
Discussion: This case discusses the importance of a rare organism in the CF population. Targeting I. limosus was key to recovery, revealing its potential pathogenicity.
Keywords: Inquilinus limosus; MRSA; cystic fibrosis; infections; nontuberculous mycobacterium.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cicatiello AG, Iula DV, Pagliuca C, et al. Identification of Inquilinus limosus in cystic fibrosis: a first report in Italy. New Microbiol. 2014; 37:567–571. - PubMed
-
- McHugh KE, Rhoads DD, Wilson DA, Highland KB, Richter SS, Procop GW. Inquilinus limosus in pulmonary disease: case report and review of the literature. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016; 86:446–449. - PubMed
-
- Schmoldt S, Latzin P, Heesemann J, Griese M, Imhof A, Hogardt M. Clonal analysis of Inquilinus limosus isolates from six cystic fibrosis patients and specific serum antibody response. J Med Microbiol. 2006; 55:1425–1433. - PubMed
-
- Jung HM, Lee JS, Bae HM, et al. Inquilinus ginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from soil of a ginseng field. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011; 61:201–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical