Reagent-Controlled Synthesis of the Branched Trisaccharide Fragment of the Antibiotic Saccharomicin B
- PMID: 29790762
- PMCID: PMC6094932
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01355
Reagent-Controlled Synthesis of the Branched Trisaccharide Fragment of the Antibiotic Saccharomicin B
Abstract
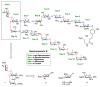
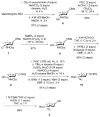
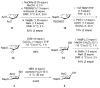
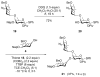
A concise synthesis of a branched trisaccharide, α-l-Dig-(1 → 3)-[α-l-Eva-(1 → 4)]-β-d-Fuc, corresponding to saccharomicin B, has been developed via reagent-controlled α-selective glycosylations. Starting from the d-fucose acceptor, l- epi-vancosamine was selectively installed using 2,3-bis(2,3,4-trimethoxyphenyl)cyclopropene-1-thione/oxalyl bromide mediated dehydrative glycosylation. Following deprotection, l-digitoxose was installed using the AgPF6/TTBP thioether-activation method to produce the trisaccharide as a single α-anomer. This highly functionalized trisaccharide can potentially serve as both a donor and an acceptor for the total synthesis of the antibiotic saccharomicin B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

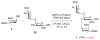
References
-
- Kong F, Zhao N, Siegel MM, Janota K, Ashcroft JS, Koehn FE, Borders DB, Carter GT. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;120:13301.
- Shi SDH, Hendrickson CL, Marshall AG, Siegel MM, Kong F, Carter GT. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 1999;10:1285.
-
- Pletcher JM, McDonald FE. Org Lett. 2005;7:4749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

