Nitrogen limitation, toxin synthesis potential, and toxicity of cyanobacterial populations in Lake Okeechobee and the St. Lucie River Estuary, Florida, during the 2016 state of emergency event
- PMID: 29791446
- PMCID: PMC5965861
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196278
Nitrogen limitation, toxin synthesis potential, and toxicity of cyanobacterial populations in Lake Okeechobee and the St. Lucie River Estuary, Florida, during the 2016 state of emergency event
Abstract
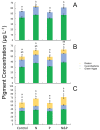
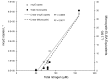
Lake Okeechobee, FL, USA, has been subjected to intensifying cyanobacterial blooms that can spread to the adjacent St. Lucie River and Estuary via natural and anthropogenically-induced flooding events. In July 2016, a large, toxic cyanobacterial bloom occurred in Lake Okeechobee and throughout the St. Lucie River and Estuary, leading Florida to declare a state of emergency. This study reports on measurements and nutrient amendment experiments performed in this freshwater-estuarine ecosystem (salinity 0-25 PSU) during and after the bloom. In July, all sites along the bloom exhibited dissolved inorganic nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios < 6, while Microcystis dominated (> 95%) phytoplankton inventories from the lake to the central part of the estuary. Chlorophyll a and microcystin concentrations peaked (100 and 34 μg L-1, respectively) within Lake Okeechobee and decreased eastwards. Metagenomic analyses indicated that genes associated with the production of microcystin (mcyE) and the algal neurotoxin saxitoxin (sxtA) originated from Microcystis and multiple diazotrophic genera, respectively. There were highly significant correlations between levels of total nitrogen, microcystin, and microcystin synthesis gene abundance across all surveyed sites (p < 0.001), suggesting high levels of nitrogen supported the production of microcystin during this event. Consistent with this, experiments performed with low salinity water from the St. Lucie River during the event indicated that algal biomass was nitrogen-limited. In the fall, densities of Microcystis and concentrations of microcystin were significantly lower, green algae co-dominated with cyanobacteria, and multiple algal groups displayed nitrogen-limitation. These results indicate that monitoring and regulatory strategies in Lake Okeechobee and the St. Lucie River and Estuary should consider managing loads of nitrogen to control future algal and microcystin-producing cyanobacterial blooms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures








References
-
- Carey C, Ibelings B, Hoffmann E, Hamilton D, Brookes J. Eco-physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012;46(5):1394–1407. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- O’Neil J, Davis T, Burford M, Gobler C. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae. 2012;14:313–334.
-
- Paerl H, Paul V. Climate change: links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012;46(5):1349–1363. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Meerhoff M, Lauridsen T, Jensen J. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction—some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia. 2007;584(1):239–252.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

