Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty with right-handed surgeons using posterolateral approach?
- PMID: 29792206
- PMCID: PMC5967059
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-018-0789-y
Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty with right-handed surgeons using posterolateral approach?
Abstract
Background: The impact of surgeon handedness on acetabular cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty (THA) is not well studied. The aim of our study is to investigate the difference of cup orientation in bilateral THA performed by right-handed surgeons using posterolateral approach and which cup could be fitter to Lewinneck's safe zone.
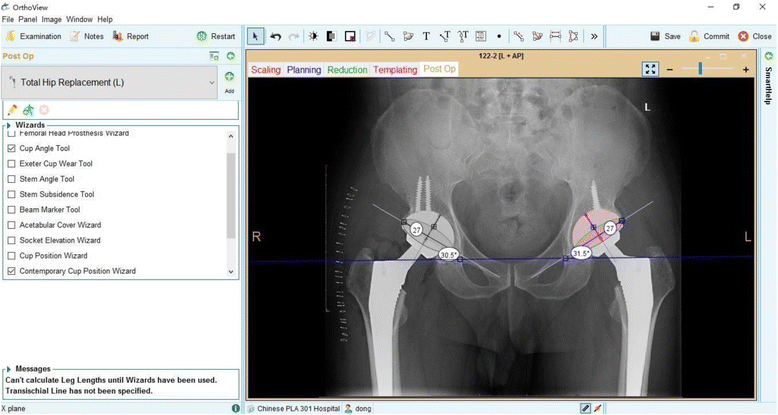
Methods: The study consisted of 498 patients that underwent bilateral THA by three right-handed surgeons in our hospital. Postoperative acetabular cup anteversion and abduction on an anteroposterior pelvic radiograph were measured by Orthoview software (Orthoview LLC, Jacksonville, Florida). Furthermore, the percentage of cup placement within the safe zone was compared.
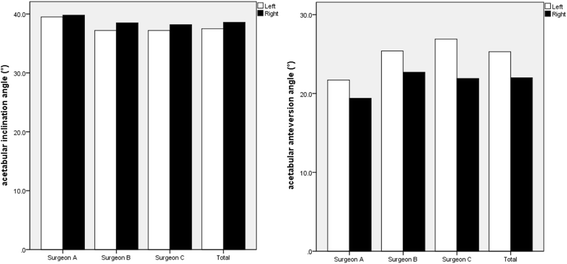
Results: The mean anteversion was 25.28 (25.28° ± 7.16°) in left THA and 22.01 (22.01° ± 6.35°) in right THA (p < 0.001). The mean abduction was 37.50 (37.50° ± 6.76°) in left THA and 38.59 (38.59° ± 6.84°) in right THA (p = 0.011). In the left side, the cup was positioned in Lewinnek's safe zone in 52% for anteversion, 87% for abduction, and 46% for both anteversion and abduction. But the cup placement within Lewinnek's safe zone was 71, 88, and 62% in the right side, respectively. There were significant differences in the percentage of acetabular cup placement within the safe zone for anteversion (p < 0.001) and for both anteversion and inclination (p < 0.001). Dislocation occurred in 7.0% (35/498) of cases in left THA and 3.2% (16/498) in right THA. The percentages of patients experiencing dislocation were significantly different between the two sides (p = 0.006).
Conclusions: This current study demonstrated that surgeon handedness is likely to be a contributing factor that affects cup inclination and anteversion in bilateral THA and that the placement of cup performed by dominant hands of surgeons is more accurate than that performed by non-dominant sides.
Keywords: Anteversion; Inclination; Safe zone; Surgeon handedness; Total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Ethics Committee of Chinese PLA General Hospital reviewed and approved this study, and written informed consent was obtained from the patients for the publication of individual clinical details and accompanying images. The study was conducted according to the ethical principles stated in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
We obtained permission from patients/participants to publish their data, and all authors consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Can a target zone safer than Lewinnek's safe zone be defined to prevent instability of total hip arthroplasties? Case-control study of 56 dislocated THA and 93 matched controls.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017 Sep;103(5):657-661. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28629942
-
The Safe Zone Range for Cup Anteversion Is Narrower Than for Inclination in THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Feb;476(2):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000051. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529664 Free PMC article.
-
What Safe Zone? The Vast Majority of Dislocated THAs Are Within the Lewinnek Safe Zone for Acetabular Component Position.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Feb;474(2):386-91. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4432-5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 26150264 Free PMC article.
-
Surgeon handedness affects the acetabular cup positioning during primary total hip arthroplasty regardless of the surgical approach. a systematic review and metanalysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Oct 7;25(1):792. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07868-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39375663 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and navigation measurement of acetabular component position in THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009 Jan;467(1):32-42. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0597-5. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. PMID: 18979147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Surgeon's handedness in direct anterior approach-hip replacement.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Aug 3;21(1):516. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03545-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32746833 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Laterality in Microsurgery: Comparative Study of an Expert and a Novice.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 2;13(13):3894. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133894. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999460 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-Assisted Total Hip Arthroplasty for Arthrodesed Hips.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020 May 4;16:357-368. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S246565. eCollection 2020. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020. PMID: 32440134 Free PMC article.
-
Lewinnek Safe Zone References are Frequently Misquoted.Arthroplast Today. 2020 Nov 26;6(4):945-953. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2020.09.011. eCollection 2020 Dec. Arthroplast Today. 2020. PMID: 33299915 Free PMC article.
-
Does the placement of acetabular cups differ between right and left sides for a right-handed surgeon operating through a direct lateral approach? A comparative study.Arthroplasty. 2024 Nov 5;6(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s42836-024-00278-8. Arthroplasty. 2024. PMID: 39497213 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

