Metabolic and Physiologic Imaging Biomarkers of the Tumor Microenvironment Predict Treatment Outcome with Radiation or a Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug in Mice
- PMID: 29792309
- PMCID: PMC8092078
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0491
Metabolic and Physiologic Imaging Biomarkers of the Tumor Microenvironment Predict Treatment Outcome with Radiation or a Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug in Mice
Abstract
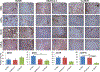
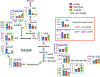
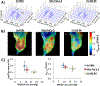
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characterized by hypoxic niches that lead to treatment resistance. Therefore, studies of tumor oxygenation and metabolic profiling should contribute to improved treatment strategies. Here, we define two imaging biomarkers that predict differences in tumor response to therapy: (i) partial oxygen pressure (pO2), measured by EPR imaging; and (ii) [1-13C] pyruvate metabolism rate, measured by hyperpolarized 13C MRI. Three human PDAC xenografts with varying treatment sensitivity (Hs766t, MiaPaCa2, and Su.86.86) were grown in mice. The median pO2 of the mature Hs766t, MiaPaCa2, and Su.86.86 tumors was 9.1 ± 1.7, 11.1 ± 2.2, and 17.6 ± 2.6 mm Hg, and the rate of pyruvate-to-lactate conversion was 2.72 ± 0.48, 2.28 ± 0.26, and 1.98 ± 0.51 per minute, respectively (n = 6, each). These results are in agreement with steady-state data of matabolites quantified by mass spectroscopy and histologic analysis, indicating glycolytic and hypoxia profile in Hs766t, MiaPaca2, and Su.86.86 tumors. Fractionated radiotherapy (5 Gy × 5) resulted in a tumor growth delay of 16.7 ± 1.6 and 18.0 ± 2.7 days in MiaPaca2 and Su.86.86 tumors, respectively, compared with 6.3 ± 2.7 days in hypoxic Hs766t tumors. Treatment with gemcitabine, a first-line chemotherapeutic agent, or the hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302 was more effective against Hs766t tumors (20.0 ± 3.5 and 25.0 ± 7.7 days increase in survival time, respectively) than MiaPaCa2 (2.7 ± 0.4 and 6.7 ± 0.7 days) and Su.86.86 (4.7 ± 0.6 and 0.7 ± 0.6 days) tumors. Collectively, these results demonstrate the ability of molecular imaging biomarkers to predict the response of PDAC to treatment with radiotherapy and TH-302.Significance: pO2 imaging data and clinically available metabolic imaging data provide useful insight into predicting the treatment efficacy of chemotherapy, radiation, and a hypoxia-activated prodrug as monotherapies and combination therapies in PDAC tumor xenograft models. Cancer Res; 78(14); 3783-92. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

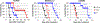

Similar articles
-
Imaging Metabolic Processes to Predict Radiation Responses.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jan;29(1):81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.10.004. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30573188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyruvate sensitizes pancreatic tumors to hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302.Cancer Metab. 2015 Jan 29;3(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40170-014-0026-z. eCollection 2015. Cancer Metab. 2015. PMID: 25635223 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pH by Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Mediates Survival of Pancreatic Cancer Cells With Activated KRAS in Response to Hypoxia.Gastroenterology. 2019 Sep;157(3):823-837. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 9. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31078621
-
MR Imaging Biomarkers to Monitor Early Response to Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug TH-302 in Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts.PLoS One. 2016 May 26;11(5):e0155289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155289. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27227903 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of tumor oxygenation and metabolic profile.Acta Oncol. 2013 Oct;52(7):1248-56. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2013.819118. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Acta Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23957619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical Applications of Multi-Platform Imaging in Animal Models of Cancer.Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;81(5):1189-1200. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0373. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33262127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal Molecular Imaging Detects Early Responses to Immune Checkpoint Blockade.Cancer Res. 2021 Jul 1;81(13):3693-3705. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3182. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33837042 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: biological hallmarks, current status, and future perspectives of combined modality treatment approaches.Radiat Oncol. 2019 Aug 8;14(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1345-6. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31395068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiparametric MRI and Coregistered Histology Identify Tumor Habitats in Breast Cancer Mouse Models.Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 1;79(15):3952-3964. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0213. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31186232 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Metabolic Processes to Predict Radiation Responses.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jan;29(1):81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2018.10.004. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30573188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hidalgo M, Von Hoff DD. Translational Therapeutic Opportunities in Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Pancreas. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4249–56. - PubMed
-
- Stathis A, Moore MJ. Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol; 2010;7:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Erkan M, Hausmann S, Michalski CW, Fingerle AA, Dobritz M, Kleeff J, et al. The role of stroma in pancreatic cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol; 2012;9:454–67. - PubMed
-
- Koong AC, Mehta VK, Le QT, Fisher GA, Terris DJ, Brown JM, et al. Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:919–22. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo Y, Ding Q, Desaki R, Maemura K, Mataki Y, Shinchi H, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha plays a pivotal role in hepatic metastasis of pancreatic cancer: an immunohistochemical study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21:105–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

