Sphingolipid changes do not underlie fatty acid-evoked GLUT4 insulin resistance nor inflammation signals in muscle cells
- PMID: 29794037
- PMCID: PMC6027910
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M080788
Sphingolipid changes do not underlie fatty acid-evoked GLUT4 insulin resistance nor inflammation signals in muscle cells
Abstract
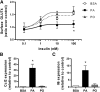
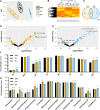
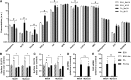
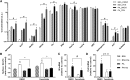
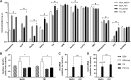
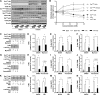
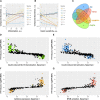
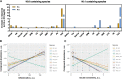
Ceramides contribute to obesity-linked insulin resistance and inflammation in vivo, but whether this is a cell-autonomous phenomenon is debated, particularly in muscle, which dictates whole-body glucose uptake. We comprehensively analyzed lipid species produced in response to fatty acids and examined the consequence to insulin resistance and pro-inflammatory pathways. L6 myotubes were incubated with BSA-adsorbed palmitate or palmitoleate in the presence of myriocin, fenretinide, or fumonisin B1. Lipid species were determined by lipidomic analysis. Insulin sensitivity was scored by Akt phosphorylation and glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation, while pro-inflammatory indices were estimated by IκBα degradation and cytokine expression. Palmitate, but not palmitoleate, had mild effects on Akt phosphorylation but significantly inhibited insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation and increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines Il6 and Ccl2 Ceramides, hexosylceramides, and sphingosine-1-phosphate significantly heightened by palmitate correlated negatively with insulin sensitivity and positively with pro-inflammatory indices. Inhibition of sphingolipid pathways led to marked changes in cellular lipids, but did not prevent palmitate-induced impairment of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation, suggesting that palmitate-induced accumulation of deleterious lipids and insulin resistance are correlated but independent events in myotubes. We propose that muscle cell-endogenous ceramide production does not evoke insulin resistance and that deleterious effects of ceramides in vivo may arise through ancillary cell communication.
Keywords: ceramides; glucose transporter 4; inflammation; lipidomics.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Summers S. A. 2018. Could ceramides become the new cholesterol? Cell Metab. 27: 276–280. - PubMed
-
- Boon J., Hoy A. J., Stark R., Brown R. D., Meex R. C., Henstridge D. C., Schenk S., Meikle P. J., Horowitz J. F., Kingwell B. A., et al. 2013. Ceramides contained in LDL are elevated in type 2 diabetes and promote inflammation and skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Diabetes. 62: 401–410. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

