Mechanism of phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination mediated by a single Legionella effector
- PMID: 29795346
- PMCID: PMC5980775
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0147-6
Mechanism of phosphoribosyl-ubiquitination mediated by a single Legionella effector
Abstract
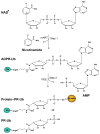
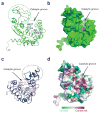
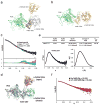
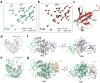
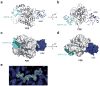
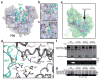
Ubiquitination is a post-translational modification that regulates many cellular processes in eukaryotes1-4. The conventional ubiquitination cascade culminates in a covalent linkage between the C terminus of ubiquitin (Ub) and a target protein, usually on a lysine side chain1,5. Recent studies of the Legionella pneumophila SidE family of effector proteins revealed a ubiquitination method in which a phosphoribosyl ubiquitin (PR-Ub) is conjugated to a serine residue on substrates via a phosphodiester bond6-8. Here we present the crystal structure of a fragment of the SidE family member SdeA that retains ubiquitination activity, and determine the mechanism of this unique post-translational modification. The structure reveals that the catalytic module contains two distinct functional units: a phosphodiesterase domain and a mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase domain. Biochemical analysis shows that the mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase domain-mediated conversion of Ub to ADP-ribosylated Ub (ADPR-Ub) and the phosphodiesterase domain-mediated ligation of PR-Ub to substrates are two independent activities of SdeA. Furthermore, we present two crystal structures of a homologous phosphodiesterase domain from the SidE family member SdeD 9 in complexes with Ub and ADPR-Ub. The structures suggest a mechanism for how SdeA processes ADPR-Ub to PR-Ub and AMP, and conjugates PR-Ub to a serine residue in substrates. Our study establishes the molecular mechanism of phosphoribosyl-linked ubiquitination and will enable future studies of this unusual type of ubiquitination in eukaryotes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

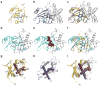




Comment in
-
Deciphering the catalytic mechanism of bacterial ubiquitination.Nature. 2018 May;557(7707):644-645. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-05250-6. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29805175 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A. Basic Medical Research Award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med. 2000;6:1073–1081. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZJ, Sun LJ. Nonproteolytic functions of ubiquitin in cell signaling. Mol Cell. 2009;33:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Haglund K, Dikic I. The role of ubiquitylation in receptor endocytosis and endosomal sorting. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Komander D, Rape M. The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:203–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

