Cross-shelf investigation of coral reef cryptic benthic organisms reveals diversity patterns of the hidden majority
- PMID: 29795402
- PMCID: PMC5967342
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-26332-5
Cross-shelf investigation of coral reef cryptic benthic organisms reveals diversity patterns of the hidden majority
Abstract
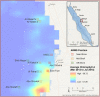
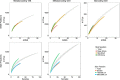
Coral reefs harbor diverse assemblages of organisms yet the majority of this diversity is hidden within the three dimensional structure of the reef and neglected using standard visual surveys. This study uses Autonomous Reef Monitoring Structures (ARMS) and amplicon sequencing methodologies, targeting mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I and 18S rRNA genes, to investigate changes in the cryptic reef biodiversity. ARMS, deployed at 11 sites across a near- to off-shore gradient in the Red Sea were dominated by Porifera (sessile fraction), Arthropoda and Annelida (mobile fractions). The two primer sets detected different taxa lists, but patterns in community composition and structure were similar. While the microhabitat of the ARMS deployment affected the community structure, a clear cross-shelf gradient was observed for all fractions investigated. The partitioning of beta-diversity revealed that replacement (i.e. the substitution of species) made the highest contribution with richness playing a smaller role. Hence, different reef habitats across the shelf are relevant to regional diversity, as they harbor different communities, a result with clear implications for the design of Marine Protected Areas. ARMS can be vital tools to assess biodiversity patterns in the generally neglected but species-rich cryptic benthos, providing invaluable information for the management and conservation of hard-bottomed habitats over local and global scales.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Legendre P, Borcard D, Peres-Neto PR. Analyzing beta diversity: partitioning the spatial variation of community composition data. Ecological Monographs. 2005;75:435–450.
-
- Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP. How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 2016;31:67–80. - PubMed
-
- Cleary D, et al. Variation in the composition of corals, fishes, sponges, echinoderms, ascidians, molluscs, foraminifera and macroalgae across a pronounced in-to-offshore environmental gradient in the Jakarta Bay–Thousand Islands coral reef complex. Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2016;110:701–717. - PubMed
-
- Cleary DF, et al. Relating variation in species composition to environmental variables: a multi-taxon study in an Indonesian coral reef complex. Aquatic Sciences-Research Across Boundaries. 2008;70:419–431.
-
- Cleary DFR, et al. Variation in the diversity and composition of benthic taxa as a function of distance offshore, depth and exposure in the Spermonde Archipelago, Indonesia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2005;65:557–570.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

