What Do You Get from DNA-Encoded Libraries?
- PMID: 29795750
- PMCID: PMC5949729
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00128
What Do You Get from DNA-Encoded Libraries?
Abstract
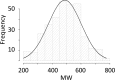
Use of DNA-encoded libraries (DELs) in the pharmaceutical industry has rapidly increased. We discuss what to expect when you run a DEL screen and contemplate guidelines for library design. Additionally, we consider some visionary work and extrapolate to the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Harris P. A.; Berger S. B.; Jeong J. U.; Nagilla R.; Bandyopadhyay D.; Campobasso N.; Capriotti C. A.; Cox J. A.; Dare L.; Dong X.; Eidam P. M.; Finger J. N.; Hoffman S. J.; Kang J.; Kasparcova V.; King B. W.; Lehr R.; Lan Y.; Leister L. K.; Lich J. D.; MacDonald T. T.; Miller N. A.; Ouellette M. T.; Pao C. S.; Rahman A.; Reilly M. A.; Rendina A. R.; Rivera E. J.; Schaeffer M. C.; Sehon C. A.; Singhaus R. R.; Sun H. H.; Swift B. A.; Totoritis R. D.; Vossenkämper A.; Ward P.; Wisnoski D. D.; Zhang D.; Marquis R. W.; Gough P. J.; Bertin J. Discovery of a First-in-Class Receptor Interacting Protein 1 (RIP1) Kinase Specific Clinical Candidate (GSK2982772) for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1247–1261. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01751. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clark M. A.; Acharya R. A.; Arico-Muendel C. C.; Belyanskaya S. L.; Benjamin D. R.; Carlson N. R.; Centrella P. A.; Chiu C. H.; Creaser S. P.; Cuozzo J. W.; Davie C. P.; Ding Y.; Franklin G. J.; Franzen K. D.; Gefter M. L.; Hale S. P.; Hansen N. J. V.; Israel D. I.; Jiang J.; Kavarana M. J.; Kelley M. S.; Kollmann C. S.; Li F.; Lind K.; Mataruse S.; Medeiros P. F.; Messer J. A.; Myers P.; O’Keefe H.; Oliff M. C.; Rise C. E.; Satz A. L.; Skinner S. R.; Svendsen J. L.; Tang L.; van Vloten K.; Wagner R. W.; Yao G.; Zhao B.; Morgan B. A. Design, synthesis and selection of DNA-encoded small molecule libraries. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 647–654. 10.1038/nchembio.211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eidam O.; Satz A. L. Analysis of the Productivity of DNA Encoded Libraries. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 1323–1331. 10.1039/C6MD00221H. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources