Molecular Characterization and Directed Evolution of a Metagenome-Derived l-Cysteine Sulfinate Decarboxylase
- PMID: 29796005
- PMCID: PMC5956266
- DOI: 10.17113/ftb.56.01.18.5415
Molecular Characterization and Directed Evolution of a Metagenome-Derived l-Cysteine Sulfinate Decarboxylase
Abstract
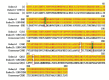
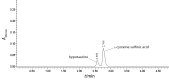
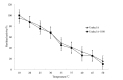
l-Cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase (CSD, EC 4.1.1.29), the rate-limiting enzyme in taurine synthesis pathway, catalyzes l-cysteine sulfinic acid to form hypotaurine. Identification of the novel CSD that could improve the biosynthetic efficiency of taurine is important. An unexplored decarboxylase gene named undec1A was identified in a previous work through sequence-based screening of uncultured soil microorganisms. Random mutagenesis through sequential error-prone polymerase chain reaction was used in Undec1A. A mutant Undec1A-1180, which was obtained from mutagenesis library, had 5.62-fold higher specific activity than Undec1A at 35 °C and pH=7.0. Molecular docking results indicated that amino acid residues Ala235, Val237, Asp239, Ile267, Ala268, and Lys298 in the Undec1A-1180 protein helped recognize and catalyze the substrate molecules of l-cysteine sulfinic acid. These results could serve as a basis for elucidating the characteristics of the Undec1A-1180. Directed evolution technology is a convenient way to improve the biotechnological applications of metagenome-derived genes.
Keywords: l-cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase; metagenomic library; sequential error-prone PCR; taurine.
Figures

References
-
- Gu Y, Shi F, Yang H, Deng Y. Leaching separation of taurine and sodium sulfate solid mixture using ionic liquids. Separ Purif Tech. 2004;35:153–9. 10.1016/j.seppur.2003.08.004 - DOI
-
- Haga Y, Kondo H, Kumagai A, Satoh N, Hirono I, Satoh S. Isolation, molecular characterization of cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSD) of red sea bream Pagrus major and yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata and expression analysis of CSD from several marine fish species. Aquaculture. 2015;449:8–17. 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.04.004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
