Relative Afferent Pupillary Defects in Homonymous Visual Field Defects Caused by Stroke of the Occipital Lobe Using Pupillometer
- PMID: 29796045
- PMCID: PMC5958967
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2017.1367012
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defects in Homonymous Visual Field Defects Caused by Stroke of the Occipital Lobe Using Pupillometer
Abstract
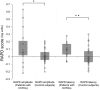
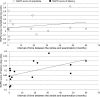
Relative afferent pupillary defects (RAPD) may be detected in patients with occipital lobe lesions. However, no previous report has used an objective technique to record the abnormal pupillary light reflex in such cases. Therefore, we measured the pupillary light reflex objectively in 15 patients with homonymous visual field defects (HVFD) due to occipital stroke using a new pupillometer. This study detected significantly smaller and slower pupillary light reflexes in the contralateral eyes than in the other eyes, which is equivalent to the presence of RAPD in patients with HVFDs caused by retrogeniculate lesions using an objective technique. Our results confirmed those of the previous reports using the swinging flashlight test more objectively.
Keywords: Amplitude; latency; pupillary light reflex pathway; pupillometer; retrograde trans-synaptic degeneration.
Figures
References
-
- Wernicke C. Über hemianopische pupillenreaktion. 1883;1:49–53.
-
- Wilhelm H, Wilhelm B, Petersen D, Schmidt U, Schiefer U. Relative afferent pupillary defects in patients with geniculate and retrogeniculate lesions. 1996;16:219–224. doi: 10.3109/01658109609044629. - DOI
-
- Papageorgiou E, Ticini LF, Hardiess G, Schaeffel F, Wiethoelter H, Mallot HA, Bahlo S, Wilhelm B, Vonthein R, Schiefer U, Karnath HO. The pupillary light reflex pathway: cytoarchitectonic probabilistic maps in hemianopic patients. 2008;70:956–963. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000305962.93520.ed. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
