Diagnostic accuracy of Onen's Alternative Grading System combined with Doppler evaluation of ureteral jets as an alternative in the diagnosis of obstructive hydronephrosis in children
- PMID: 29796345
- PMCID: PMC5961622
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4791
Diagnostic accuracy of Onen's Alternative Grading System combined with Doppler evaluation of ureteral jets as an alternative in the diagnosis of obstructive hydronephrosis in children
Abstract
Introduction: Ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) is a common congenital anomaly leading to varying degrees of hydronephrosis (HN), ranging from no apparent effect on the renal function to atrophy. Evaluation of these children is based on Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy (DRS) and Ultrasonography (US). Recent studies have suggested that new parameters of conventional and color Doppler ultrasonography (CDUS) may be useful in discriminating which kidneys are obstructed. The present study aims to assess the diagnostic accuracy of such parameters in the diagnosis of obstruction in children with UPJO.
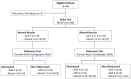
Methods: We evaluated 44 patients (33 boys) with a mean age of 6.53 ± 4.39 years diagnosed with unilateral high-grade hydronephrosis (SFU grades 3 and 4). All underwent DRS and index tests (conventional US and CDUS to evaluate ureteral jets frequency) within a maximum interval of two weeks. Hydronephrotic units were reclassified according to the alternative grading system (AGS) proposed by Onen et al. Obstruction in the DRS was defined as a differential renal function <40% on the affected side and/or features indicating poor drainage function like T1/2 >20 minutes after the administration of furosemide, and a plateau or ascending pattern of the excretion curve.
Results: Nineteen hydronephrotic units (43.1%) were obstructed. Some degree of cortical atrophy-grades 3 (segmental) or 4 (diffuse)-was present in those obstructed units. AGS grades had 100% sensitivity, 76% of specificity and 86.4% of accuracy. The absence of ureteral jets had a sensitivity of 73.68%, a specificity of 100% with an accuracy of 88.6%. When we analyzed the two aspects together and considered obstructed the renal units classified as AGS grade 3 or 4 with no jets, sensitivity increased to 78.9%, accuracy to 92%, remaining with a maximum specificity of 100%. These features combined would allow us to avoid performing DRS in 61% of our patients, leaving more invasive tests to inconclusive cases.
Conclusions: Although DRS remains the mainstay to distinguishing obstructive from non-obstructive kidneys, grade of hydronephrosis and frequency of ureteral jets, independently or in combination may be a reliable alternative in the mostly cases.This alternative approach has high accuracy, it is less invasive, easily reproducible and may play a role in the diagnosis of obstruction in pediatric population.
Keywords: Children; Diagnostic test; Diuretic renogram; Doppler ultrasound; Grading system; Hydronephrosis; Ureteral jets; Urinary tract obstruction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Grading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge.Front Pediatr. 2020 Aug 27;8:458. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00458. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32984198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of color Doppler sonographic study of the ureteric jets in evaluation of hydronephrosis.J Pediatr Urol. 2008 Apr;4(2):113-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2007.10.013. Epub 2008 Jan 14. J Pediatr Urol. 2008. PMID: 18631905 Clinical Trial.
-
Diuresis renal scintigraphy "F-0" in diagnosing of upper urinary tract obstruction in children: the clinical significance.Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2005;8(1):21-7. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur. 2005. PMID: 15977143
-
Doppler visualization of ureteric jets in unilateral hydronephrosis in children and adolescents.Eur J Radiol. 2001 Sep;39(3):209-14. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00329-1. Eur J Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11566251
-
Urinary biomarkers in hydronephrosis.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4582. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461995 Review.
Cited by
-
Antegrade Ureteral Stenting in Pediatric Patients: Introducing a Novel Ureteral Morphological Classification and a New Perspective on Functional Success.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 3;14(1):246. doi: 10.3390/jcm14010246. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39797327 Free PMC article.
-
Grading of Hydronephrosis: An Ongoing Challenge.Front Pediatr. 2020 Aug 27;8:458. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00458. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32984198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of robot-assisted laparoscopy and ureteroscopy for the management of complex ureteral strictures.BMC Urol. 2023 Oct 12;23(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01333-3. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 37828507 Free PMC article.
-
Diuretic Enhanced Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Pyeloureteral Obstruction.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Oct 3;55(10):670. doi: 10.3390/medicina55100670. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31623344 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: Ultrasound-Based Scoring System for Indication of Pyeloplasty in Patients With UPJO-Like Hydronephrosis.Front Pediatr. 2020 Dec 3;8:594527. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.594527. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33344385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, De Vet HC, Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD initiative. Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy. Clinical Chemistry. 2003;49:1–6. doi: 10.1373/49.1.1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Erickson BA, Maizels M, Shore RM, Pazona JF, Hagerty JA, Yerkes EB, Chaviano AH, Kaplan WE, Cheng EY. Newborn society of fetal urology grade 3 hydronephrosis is equivalent to preserved percentage differential function. Journal of Pediatric Urology. 2007;3:382–386. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2007.01.196. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources