Amino Acid- and Insulin-Induced Activation of mTORC1 in Neonatal Piglet Skeletal Muscle Involves Sestin2-GATOR2, Rag A/C-mTOR, and RHEB-mTOR Complex Formation
- PMID: 29796625
- PMCID: PMC6669959
- DOI: 10.1093/jn/nxy044
Amino Acid- and Insulin-Induced Activation of mTORC1 in Neonatal Piglet Skeletal Muscle Involves Sestin2-GATOR2, Rag A/C-mTOR, and RHEB-mTOR Complex Formation
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Nutr. 2019 Jun 1;149(6):1097. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz057. J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31149707 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Feeding stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of neonates and this response is regulated through activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). The identity of signaling components that regulate mTORC1 activation in neonatal muscle has not been fully elucidated.
Objective: We investigated the independent effects of the rise in amino acids (AAs) and insulin after a meal on the abundance and activation of potential regulators of mTORC1 in muscle and whether the responses are modified by development.
Methods: Overnight-fasted 6- and 26-d-old pigs were infused for 2 h with saline (control group) or with a balanced AA mixture (AA group) or insulin (INS group) to achieve fed levels while insulin or AAs, respectively, and glucose were maintained at fasting levels. Muscles were analyzed for potential mTORC1 regulatory mechanisms and results were analyzed by 2-factor ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
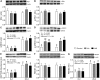
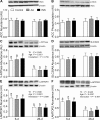
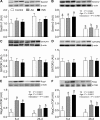
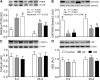
Results: The abundances of DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR), growth factor receptor bound protein 10 (GRB10), and regulated in development and DNA damage response 2 (REDD2) were lower (65%, 73%, and 53%, respectively; P < 0.05) and late endosomal/lysosomal adaptor, MAPK and mTOR activator 1/2 (LAMTOR1/2), vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase), and Sestrin2 were higher (94%, 141%, 145%, and 127%, respectively; P < 0.05) in 6- than in 26-d-old pigs. Both AA and INS groups increased phosphorylation of GRB10 (P < 0.05) compared with control in 26- but not in 6-d-old pigs. Formation of Ras-related GTP-binding protein A (RagA)-mTOR, RagC-mTOR, and Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB)-mTOR complexes was increased (P < 0.05) and Sestrin2-GTPase activating protein activity towards Rags 2 (GATOR2) complex was decreased (P < 0.05) by both AA and INS groups and these responses were greater (P < 0.05) in 6- than in 26-d-old pigs.
Conclusion: The results suggest that formation of RagA-mTOR, RagC-mTOR, RHEB-mTOR, and Sestrin2-GATOR2 complexes may be involved in the AA- and INS-induced activation of mTORC1 in skeletal muscle of neonates after a meal and that enhanced activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway in neonatal muscle is in part due to regulation by DEPTOR, GRB10, REDD2, LAMTOR1/2, V-ATPase, and Sestrin2.
Figures

References
-
- Proud CG. Regulation of protein synthesis by insulin. Biochem Soc Trans 2006;34:213–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

