FFAR4 Is Involved in Regulation of Neurotensin Release From Neuroendocrine Cells and Male C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 29796668
- PMCID: PMC6486825
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2018-00284
FFAR4 Is Involved in Regulation of Neurotensin Release From Neuroendocrine Cells and Male C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
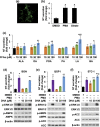
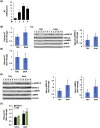
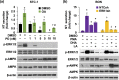
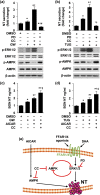
Neurotensin (NT), a 13 amino-acid peptide, is predominantly released from enteroendocrine cells of the small bowel in response to fat ingestion. Free fatty acid receptors (FFARs) FFAR1 and FFAR4 regulate secretion of gut hormones and insulin. Here, we show that docosahexaenoic acid, a long-chain fatty acid, has the most dramatic effect on NT release. FFAR1 agonists slightly stimulate and FFAR4 agonists dramatically stimulate and amplify NT secretion. Double knockdown of FFAR1 and FFAR4 decreases NT release, whereas overexpression of FFAR4, but not FFAR1, increases NT release. Administration of cpdA, an FFAR4 agonist, but not TAK-875, a selective FFAR1 agonist, increases plasma NT levels and further increases olive oil-stimulated plasma NT levels. Inhibition of MAPK kinase (MEK)/ERK1/2 decreased fatty acid-stimulated NT release but increased AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation. In contrast, inhibition of AMPK further increased NT secretion and ERK1/2 phosphorylation mediated by FFAR1 or FFAR4. Our results indicate that FFAR4 plays a more critical role than FFAR1 in mediation of fat-regulated NT release and in inhibitory crosstalk between MEK/ERK1/2 and AMPK in the control of NT release downstream of FFAR1 and FFAR4.
Figures


References
-
- Carraway R, Leeman SE. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973;248(19):6854–6861. - PubMed
-
- Barber DL, Cacace AM, Raucci DT, Ganz MB. Fatty acids stereospecifically stimulate neurotensin release and increase [Ca2+]i in enteric endocrine cells. Am J Physiol. 1991;261(3 Pt 1):G497–G503. - PubMed
-
- Ferris CF, Carraway RE, Hammer RA, Leeman SE. Release and degradation of neurotensin during perfusion of rat small intestine with lipid. Regul Pept. 1985;12(2):101–111. - PubMed
-
- Polak JM, Sullivan SN, Bloom SR, Buchan AM, Facer P, Brown MR, Pearse AG. Specific localisation of neurotensin to the N cell in human intestine by radioimmunoassay and immunocytochemistry. Nature. 1977;270(5633):183–184. - PubMed
-
- Rosell S, Rökaeus A. The effect of ingestion of amino acids, glucose and fat on circulating neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979;107(3):263–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

