Regulatory RNA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, back to basics
- PMID: 29796669
- PMCID: PMC7615687
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/fty035
Regulatory RNA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, back to basics
Abstract
Since the turn of the millenium, RNA-based control of gene expression has added an extra dimension to the central dogma of molecular biology. Still, the roles of Mycobacterium tuberculosis regulatory RNAs and the proteins that facilitate their functions remain elusive, although there can be no doubt that RNA biology plays a central role in the baterium's adaptation to its many host environments. In this review, we have presented examples from model organisms and from M. tuberculosis to showcase the abundance and versatility of regulatory RNA, in order to emphasise the importance of these 'fine-tuners' of gene expression.
Figures
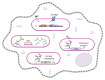


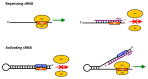

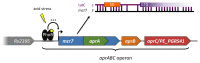
References
-
- Argaman L, Hershberg R, Vogel J, Bejerano G, Wagner EG, Margalit H, Altuvia S. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic regions of Escherichia coli. Curr Biol. 2001;11:941–950. - PubMed
-
- Arnvig KB, Young DB. Regulation of pathogen metabolism by small RNA. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 2010;7:e19–e24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

