A hyaluronic acid- and chondroitin sulfate-based medical device improves gastritis pain, discomfort, and endoscopic features
- PMID: 29796851
- PMCID: PMC6133073
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-018-0531-7
A hyaluronic acid- and chondroitin sulfate-based medical device improves gastritis pain, discomfort, and endoscopic features
Abstract
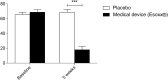
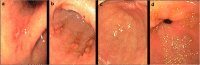
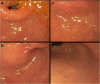
Gastritis is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of a medical device, Esoxx®, based on hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate on gastritis-related upper abdominal pain/discomfort and endoscopic features. Fifty patients, affected by gastritis, were randomised to receive the medical device or placebo. The primary endpoint was the medical device efficacy on upper abdominal pain/discomfort associated with gastritis and measured by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS). The secondary endpoints were the efficacy of the medical device on gastritis-related mucosal erosions, blood oozing, and hyperemia (redness)/edema, as assessed by endoscopy, and the patients' rating of their compliance with the treatments. A significant reduction in VAS pain was observed in the treatment group after a 5-week treatment, if compared with placebo (p < 0.001). In summary, administration of a medical device, based on hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate, improves gastritis-related upper abdominal pain/discomfort and decreases mucosal erosions, blood oozing, and hyperemia (redness)/edema at 5-week follow-up in patients affected by gastritis.
Keywords: Chondroitin sulfate; Discomfort; Endoscopy; Gastritis; Hyaluronic acid; Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of the data included in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized, open-label, multicenter study of the efficacy and safety of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate versus dimethyl sulfoxide in women with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Apr;36(4):1178-1186. doi: 10.1002/nau.23091. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 27654012 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of highly concentrated hyaluronic acid/chondroitin sulphate instillation on ureteric stent-induced discomfort after ureteroscopic lithotripsy: a multicentre randomised controlled pilot study.BJU Int. 2018 Nov;122(5):858-865. doi: 10.1111/bju.14392. Epub 2018 Jun 25. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29772114 Clinical Trial.
-
Morphological changes of bladder mucosa in patients who underwent instillation with combined sodium hyaluronic acid-chondroitin sulphate (Ialuril®).Urol Int. 2013;91(1):81-8. doi: 10.1159/000345047. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Urol Int. 2013. PMID: 23485915
-
Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate alone and in combination for urinary tract infection: assessment of protective effects in a rat model.Int J Urol. 2012 Dec;19(12):1108-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03109.x. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Int J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22852837
-
[Available evidence about efficacy of different restoring agents of glycosaminoglycans for intravesical use in interstitial cystitis].Actas Urol Esp. 2013 Feb;37(2):92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.acuro.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Actas Urol Esp. 2013. PMID: 23260184 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
A Cross-Sectional Study on Gastric Diseases and FGIDs in Bangladesh: Insights Into Causes, Symptoms, and Medications.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;8(8):e71188. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71188. eCollection 2025 Aug. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40843386 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Hyaluronic Acid and Chondroitin Sulphate-Based Medical Device Combined with Acid Suppression in the Treatment of Atypical Symptoms in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 29;11(7):1890. doi: 10.3390/jcm11071890. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35407497 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanosystems for CD44 Mediated Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 14;24(8):7286. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087286. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate-based medical devices: formulations, esophageal mucosal protection, and their place in the management of GERD.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 11;18:17562848251337822. doi: 10.1177/17562848251337822. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40520453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 61-Year-Old Woman with Chronic Iron-Deficiency Anemia Due to a Cameron Lesion and a Response to Oral Application of Combined Poloxamer 407 with Hyaluronic Acid and Chondroitin Sulfate Following Single Treatment with Pantoprazole: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2021 Jan 21;22:e928021. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.928021. Am J Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33473099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marcial G, Rodríguez C, Medici M, de Valdez GF. New approaches in gastritis treatment, gastritis and gastric cancer. In: Tonino P, editor. New insights in gastroprotection, diagnosis and treatments. Croatia - EUROPEAN UNION: InTech Publisher; 2011. pp. 153–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

