Stress, Motivation, and the Gut-Brain Axis: A Focus on the Ghrelin System and Alcohol Use Disorder
- PMID: 29797564
- PMCID: PMC6252147
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13781
Stress, Motivation, and the Gut-Brain Axis: A Focus on the Ghrelin System and Alcohol Use Disorder
Abstract
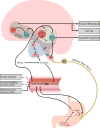
Since its discovery, the gut hormone, ghrelin, has been implicated in diverse functional roles in the central nervous system. Central and peripheral interactions between ghrelin and other hormones, including the stress-response hormone cortisol, govern complex behavioral responses to external cues and internal states. By acting at ventral tegmental area dopaminergic projections and other areas involved in reward processing, ghrelin can induce both general and directed motivation for rewards, including craving for alcohol and other alcohol-seeking behaviors. Stress-induced increases in cortisol seem to increase ghrelin in the periphery, suggesting a pathway by which ghrelin influences how stressful life events trigger motivation for rewards. However, in some states, ghrelin may be protective against the anxiogenic effects of stressors. This critical review brings together a dynamic and growing literature, that is, at times inconsistent, on the relationships between ghrelin, central reward-motivation pathways, and central and peripheral stress responses, with a special focus on its emerging role in the context of alcohol use disorder.
Keywords: Alcohol Craving; Ghrelin; Motivation; Reward Processing; Stress.
Copyright © 2018 Research Society on Alcoholism. This article has been contributed to by US Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures
References
-
- ADDOLORATO G, CAPRISTO E, LEGGIO L, FERRULLI A, ABENAVOLI L, MALANDRINO N, FARNETTI S, DOMENICALI M, D’ANGELO C, VONGHIA L, MIRIJELLO A, CARDONE S, GASBARRINI G. Relationship between ghrelin levels, alcohol craving, and nutritional status in current alcoholic patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006;30:1933–7. - PubMed
-
- AKKISI KUMSAR N, DILBAZ N. Relationship between craving and ghrelin, adiponectin, and resistin levels in patients with alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015;39:702–9. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSON AK, PHELPS EA. Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events. Nature. 2001;411:305–309. - PubMed
-
- ASAKAWA A, INUI A, KAGA T, YUZURIHA H, NAGATA T, FUJIMIYA M, KATSUURA G, MAKINO S, FUJINO MA, KASUGA M. A role of ghrelin in neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to stress in mice. Neuroendocrinology. 2001a;74:143–7. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

