[Comparative study on differences in acetabular position during total hip arthroplasty between by direct anterior approach and by posterolateral approach]
- PMID: 29798520
- PMCID: PMC8498149
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.201701036
[Comparative study on differences in acetabular position during total hip arthroplasty between by direct anterior approach and by posterolateral approach]
Abstract
Objective: To compare the differences in acetabular position during total hip arthroplasty (THA) between by direct anterior approach and by posterolateral approach.
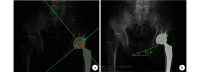
Methods: Between December 2008 and December 2015, 102 patients undergoing THA were included in the study. THA was performed by anterior approach in 51 cases (anterior group) and by posterolateral approach in 51 cases (posterolateral group). There was no significant difference in gender, age, body mass index, side, and cause of illness between 2 groups ( P>0.05), with comparability. The acetabular abduction angle and anteversion angel were measured on the X-ray film at 1 day after operation to evaluate whether the acetabular prosthesis was displaced in the safe zone.
Results: The acetabular abduction angle was (42.28±5.77)° in the anterior group and was (43.93±7.44)° in the posterolateral group, showing no significant difference ( t=1.30, P=0.19). The acetabular anteversion angle was (21.14±5.17)° in the anterior group and was (21.05±4.10)° in the posterolateral group, showing no significant difference ( t=0.05, P=0.96). The ratio in the target safe zone of the acetabular abduction angle in the anterior group and the posterolateral group were 88.2% (45/51) and 84.3% (43/51) respectively, showing no significant difference ( χ2=0.33, P=0.56). The ratio in the target safe zone of the acetabular anteversion was 80.4% (41/51) in the anterior group and was 82.4% (42/51) in the posterolateral group, showing no significant difference between 2 groups ( χ2=0.06, P=0.79). The ratio in the target safe zone of both the abduction and anteversion angel was 70.6% (36/51) in the anterior group and was 68.6% (35/51) in the posterolateral group, showing no significant difference ( χ2=0.05, P=0.82).
Conclusion: There is no differences in the acetabulum position during THA between by direct anterior approach and posterolateral approach.
目的: 比较直接前方入路与传统后外侧入路行人工全髋关节置换术后髋臼假体位置的差异。.
方法: 将 2008 年 12 月—2015 年 12 月收治并符合选择标准的 102 例行人工全髋关节置换术患者纳入研究;置换术中采用直接前方入路 51 例(直接前方入路组)、后外侧入路 51 例(后外侧入路组)。两组患者性别、年龄、体质量指数、髋别、病因等一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05),具有可比性。于术后第 1 天患者骨盆正位 X 线片测量髋臼外展角及前倾角,并根据以上两指标评价髋臼假体是否位于安全区域。.
结果: 直接前方入路组髋臼外展角和前倾角分别为(42.28±5.77)、(21.14±5.17)°,后外侧入路组分别为(43.93±7.44)、(21.05±4.10)°,比较差异均无统计学意义( t=1.30, P=0.19; t=0.05, P=0.96)。直接前方入路组髋臼外展角、前倾角位于安全区域比例分别为 88.2%(45/51)、80.4%(41/51),后外侧入路组为 84.3%(43/51)、82.4%(42/51),比较差异均无统计学意义( χ2=0.33, P=0.56; χ2=0.06, P=0.79)。直接前方入路组髋臼外展角及前倾角均在安全区域的比例为 70.6%(36/51),后外侧入路组为 68.6%(35/51),比较差异无统计学意义( χ2=0.05, P=0.82)。.
结论: 采用直接前方入路或后外侧入路行人工全髋关节置换术,髋臼假体位置无明显差异。.
Keywords: Total hip arthroplasty; acetabular position; direct anterior approach; posterolateral approach.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[USE OF SMARTPHONE IN ACETABULAR COMPONENT ANGLE MEASUREMENT DURING TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Sep 8;30(9):1061-1064. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20160216. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29786355 Chinese.
-
[Short-term effectiveness of Mako robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty via posterolateral approach].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 15;35(10):1227-1232. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202105120. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34651473 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Is the cup orientation different in bilateral total hip arthroplasty with right-handed surgeons using posterolateral approach?J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 May 23;13(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0789-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29792206 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Pelvic Tilt on the Anteversion Angle of the Acetabular Prosthesis.Orthop Surg. 2019 Oct;11(5):762-769. doi: 10.1111/os.12543. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 31663281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress on positioning accuracy of acetabulum prosthesis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016 Aug 25;29(8):770-773. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2016.08.020. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016. PMID: 29282941 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
[Application of preoperative digital-template planning in total hip arthroplasty via direct anterior approach].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Nov 15;33(11):1374-1378. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201903108. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31650751 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Restrepo C, Parvizi J, Pour AE, et al Prospective randomized study of two surgical approaches for total hip arthroplasty. J Arth-roplasty. 2010;25(5):671–9.e1. - PubMed
-
- Bertin KC, Röttinger H Anterolateral mini-incision hip replacement surgery: a modified Watson-Jones approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(429):248–255. - PubMed
-
- Agten CA, Sutter R, Dora C, et al MR imaging of soft tissue alterations after total hip arthroplasty: comparison of classic surgical approaches. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(3):1312–1321. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical