Preclinical evaluation of novel PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor SN202 as potential anti-renal cancer agent
- PMID: 29799306
- PMCID: PMC6301802
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1470733
Preclinical evaluation of novel PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor SN202 as potential anti-renal cancer agent
Abstract
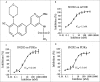
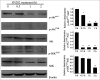
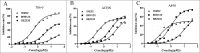
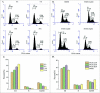
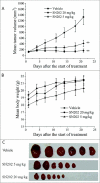
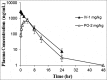
ABSTRACT The PI3K/mTOR pathway is one of the most frequently aberrantly activated pathways in human malignancies, such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and contributes to resistance to antitumor therapies. Thus, PI3K/mTOR is an attractive target for the development of antitumor agents. In this study, we evaluated the preclinical effects of a novel inhibitor SN202. We examined Akt/mTOR activities in renal cancer cells after SN202 treatment. The preclinical effects of SN202 on tumor growth were evaluated in renal cancer cells in vitro and in murine xenografts in vivo. SN202 inhibits PI3Kα, PI3Kγ, and mTOR, the corresponding IC50 values were 3.2, 3.3, and 1.2 nM, respectively. In A498, 786-0, and ACHN renal cancer cell lines, SN202 inhibits cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner and significantly inhibits 786-0 cell growth. Western blot analysis revealed that SN202 decreases the phosphorylation of PI3K downstream signaling molecules, Akt and S6K, in 786-0 renal cancer cells. Furthermore, oral administration of SN202 results in significant inhibition in human renal carcinoma xenografts in nude mice and favourable pharmacokinetic properties in rats. These results suggest that SN202 might be a promising therapeutic agent against RCC as a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor.
Keywords: PI3K/mTOR inhibitor; SN202; antitumor growth; renal cell carcinoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preclinical efficacy of dual mTORC1/2 inhibitor AZD8055 in renal cell carcinoma harboring a TFE3 gene fusion.BMC Cancer. 2019 Sep 13;19(1):917. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6096-0. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31519159 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of BRD4 and PI3K-AKT by SF2523 suppresses human renal cell carcinoma cell growth.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 30;8(58):98471-98481. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21432. eCollection 2017 Nov 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29228703 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of pimasertib, a selective MEK 1/2 inhibitor, in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitors or with multi-targeted kinase inhibitors in pimasertib-resistant human lung and colorectal cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2013 Nov;133(9):2089-101. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28236. Epub 2013 May 29. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23629727
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway: an emerging treatment strategy for squamous cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Sep;40(8):980-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.06.006. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037117 Review.
-
Autophagy as a Vital Therapy Target for Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;11:518225. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.518225. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33643028 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Individualizing Systemic Therapies in First Line Treatment and beyond for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 13;12(12):3750. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123750. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33322163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors for Tumour Treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 9;13:875372. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.875372. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35614940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genetics. 2006;7(8):606–619. PMID: 16847462; doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1879. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase–AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501. PMID: 12094235; doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc839. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vara JÁF, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treatment Rev. 2004;30(2):193–204. PMID: 15023437; doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2003.07.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PRJ, Reese CB, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol. 1997;7(4):261–269. PMID: 9094314; doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00122-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
