A diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with increased life insurance premiums
- PMID: 29800243
- PMCID: PMC6102799
- DOI: 10.1093/dote/doy008
A diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis is associated with increased life insurance premiums
Abstract
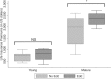
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic disease that can be diagnosed at any age, but is not associated with malignancy and does not shorten lifespan. It remains unknown whether an EoE diagnosis affects insurability or insurance premium costs. We therefore aimed to determine whether a diagnosis of EoE affects the costs of life insurance. Our investigation was a secret shopper audit study whereby we contacted national insurance companies in the United States to evaluate the effect of a diagnosis of EoE on life insurance premiums. We constructed standardized case scenarios for males and females, including a 25-year-old and a 48-year-old without other comorbid conditions, who either had or did not have a diagnosis of EoE. Companies were asked for their best estimate for a $100,000 whole life insurance policy. Comparisons between median premiums were made using the Mann-Whitney U test. There were 20 national life insurance companies contacted and a total of 73 quotes were obtained. The median premium rate was similar for EoE and non-EoE cases at the younger age ($828 [IQR $576-1,020] vs. $756 [IQR $504-$804]; P = 0.10). However, the premium for the older case without EoE was 19% less expensive compared to a case with EoE ($1990 [IQR $1,248-2,350] vs. $2,375 [IQR $2,100-2568; P = 0.02]. This finding was not explained by sex or state of residence. Based on these findings, we conclude that life insurance premiums are significantly more expensive in the older patient case with EoE when compared to the same case without EoE. Patients with EoE and their providers should be aware of the additional cost associated with this diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Dellon E S, Gonsalves N, Hirano I et al. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol 2013; 108: 679–92; quiz 93. - PubMed
-
- Schoepfer A M, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2013; 145: 1230–6e1-2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical