Hydrogen Sulfide Demonstrates Promising Antitumor Efficacy in Gastric Carcinoma by Targeting MGAT5
- PMID: 29800930
- PMCID: PMC6041565
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.04.008
Hydrogen Sulfide Demonstrates Promising Antitumor Efficacy in Gastric Carcinoma by Targeting MGAT5
Abstract
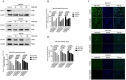
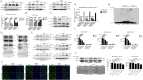
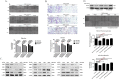
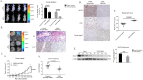
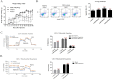
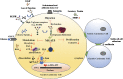
Mannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-Glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase (MGAT5) is exclusively expressed in gastric carcinoma, and plays an essential role in cancer progression, but no targeted drug is available so far. The potential anti-cancer effect of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), has not been widely recognized. It intrigued broad interest to explore the clinical benefits of cancer therapy, with the current understanding of molecular mechanisms of H2S which remains very limited. In this study, we identify that H2S is an effective inhibitor of MGAT5, leading to reduce the expression of exclusively abnormal glycoprotein processes in gastric carcinoma. H2S specifically dissociation of karyopherin subunit alpha-2 (KPNA2) with Jun proto-oncogene (c-Jun) interaction, and blocking c-Jun nuclear translocation, and downregulation of MGAT5 expression at the level of gene and protein. Consequently, H2S impairs growth and metastasis in gastric carcinoma by targeting inhibits MGAT5 activity. In an animal tumor model study, H2S is well tolerated, inhibits gastric carcinoma growth and metastasis. Our preclinical work therefore supports that H2S acts as a novel inhibitor of MGAT5 that block tumorigenesis in gastric carcinoma.
Significance: This study shows that H2S can effective targeting inhibits MGAT5 activity, and demonstrates promising antitumor efficacy. These findings gain mechanistic insights into the anti-cancer capacity of H2S and may provide useful information for the clinical explorations of H2S in cancer treatment.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Freddie B, Ahmedin J, Nathan G, Jacques F, David F. Global cancer transitions according to the Human Development Index (2008-2030): a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:790–801. - PubMed
-
- Croci DO, Cerliani JP, Dalottomoreno T, Mendezhuergo SP, Mascanfroni ID, Dergandylon S, Rabinovich GA. Glycosylation-Dependent Lectin-Receptor Interactions Preserve Angiogenesis in Anti-VEGF Refractory Tumors. Cell. 2014;156:744–758. - PubMed
-
- Granovsky M, Fata JE, Pawling J, Muller WJ, Khokha R, Dennis JW. Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis in Mgat5-deficient mice. Nat Med. 2000;6:306–312. - PubMed
-
- Partridge EA, Roy CL, Guglielmo GM, Pawling J, Cheung P, Granovsky M, Dennis JW. Regulation of cytokine receptors by Golgi N-glycan processing and endocytosis. Science. 2004;306:120–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

