Total Neoadjuvant Therapy With FOLFIRINOX Followed by Individualized Chemoradiotherapy for Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial
- PMID: 29800971
- PMCID: PMC6145728
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0329
Total Neoadjuvant Therapy With FOLFIRINOX Followed by Individualized Chemoradiotherapy for Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial
Erratum in
-
Missing Names of Co-Senior Authors.JAMA Oncol. 2018 Oct 1;4(10):1439. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4985. JAMA Oncol. 2018. PMID: 31381727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Patients with borderline-resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma have historically poor outcomes with surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy. Evaluation of a total neoadjuvant approach with highly active therapy is warranted.
Objective: To evaluate the margin-negative (R0) resection rate in borderline-resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX (fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) therapy and individualized chemoradiotherapy.
Design, setting, and participants: A single-arm, phase 2 clinical trial was conducted at a large academic hospital with expertise in pancreatic surgery from August 3, 2012, through August 31, 2016, among 48 patients with newly diagnosed, previously untreated, localized pancreatic cancer determined to be borderline resectable by multidisciplinary review, who had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0 or 1 and adequate hematologic, renal, and hepatic function. Median follow-up for the analysis was 18.0 months among the 30 patients still alive at study completion.
Interventions: Patients received FOLFIRINOX for 8 cycles. Upon restaging, patients with resolution of vascular involvement received short-course chemoradiotherapy (5 Gy × 5 with protons) with capecitabine. Patients with persistent vascular involvement received long-course chemoradiotherapy with fluorouracil or capecitabine.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary outcome was R0 resection rate; secondary outcomes were median progression-free survival (PFS) and median overall survival (OS).
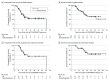
Results: Of the 48 eligible patients, 27 were men and 21 were women, with a median age of 62 years (range, 46-74 years). Of the 43 patients who planned to receive 8 preoperative cycles of chemotherapy, 34 (79%) were able to complete all cycles. Twenty-seven patients (56%) had short-course chemoradiotherapy, while 17 patients (35%) had long-course chemoradiotherapy. R0 resection was achieved in 31 of the 48 eligible patients (65%; 95% CI, 49%-78%). Among the 32 patients who underwent resection, the R0 resection rate was 97% (n = 31). Median PFS among all eligible patients was 14.7 months (95% CI, 10.5 to not reached), with 2-year PFS of 43%; median OS was 37.7 months (95% CI, 19.4 to not reached), with 2-year OS of 56%. Among patients who underwent resection, median PFS was 48.6 months (95% CI, 14.4 to not reached) and median OS has not been reached, with a 2-year PFS of 55% and a 2-year OS of 72%.
Conclusions and relevance: Preoperative FOLFIRINOX followed by individualized chemoradiotherapy in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer results in high rates of R0 resection and prolonged median PFS and median OS, supporting ongoing phase 3 trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01591733.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Gastrointestinal Cancers: Fine-Tuning the Management of Rectal, Esophageal, and Pancreas Cancers.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019 Sep 1;105(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.04.037. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019. PMID: 31422802 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(11):1039-1049. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN guidelines. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Accessed March 15, 2018.
-
- Arvold ND, Ryan DP, Niemierko A, et al. Long-term outcomes of neoadjuvant chemotherapy before chemoradiation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2012;118(12):3026-3035. - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, et al. ; Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of Unicancer; PRODIGE Intergroup . FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1817-1825. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

